ADVENTUROUS TEACHING STARTS HERE.
Cultivating Critical Thinkers: My Approach to Teaching Literature
As an educator, I've always been passionate about instilling critical thinking skills in my students. It's a topic that I recently had the opportunity to reflect on during a professional development session, and I want to share with you the insights and strategies that I believe are essential for deep engagement in the classroom.
Cultivating Critical Thinkers: My Approach to Teaching Literature
As an educator, I've always been passionate about instilling critical thinking skills in my students. It's a topic that I recently had the opportunity to reflect on during a professional development session, and I want to share with you the insights and strategies that I believe are essential for deep engagement in the classroom.
Challenging the Status Quo
During a recent PD session, I found myself in a bit of a controversial spot. I questioned a fellow teacher's approach to curriculum, which led to a broader discussion about our roles as educators. It's crucial for us to think like our students and to prioritize deep critical thinking over simply entertaining them. We need to focus on developing skills that lead to deeper critical thinking and provide opportunities for students to engage authentically with the material.
Teaching Literature Beyond Comprehension
When it comes to teaching literature, my approach might be a little unconventional. I steer clear of recall-based or plot-based activities. Instead, I encourage students to seek out summaries on their own and focus on the bigger issues at hand. It's about letting go of the minor details and teaching students to read for big picture connections. Comprehension is important, but it shouldn't be the primary focus. We should be guiding our students to think critically about broader themes and societal issues.
The Power of Close Reading
Close reading is a significant part of my teaching strategy. It's not about getting through an entire novel; it's about diving deep into passages and analyzing them. This mirrors adult book club discussions where despite different levels of recall, everyone can contribute meaningfully to the conversation. Close reading fosters a collective understanding of the text and teaches students valuable rhetorical and literary analysis skills.
Pairing Texts and Media for Enhanced Engagement
I'm a big advocate for pairing contrasting texts and media to stimulate critical thinking. For instance, combining literature with podcasts or other media that address relevant societal issues can create a dynamic learning environment. This approach encourages students to engage critically with the material and see the connections between the text and the world around them.
Visuals and Hands-On Activities
Incorporating visuals and hands-on activities is another way to enhance metaphorical thinking and create moments for critical thinking in the classroom. These methods help students to visualize and interact with the concepts in a tangible way, further deepening their understanding and engagement.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Deep Engagement
My approach to teaching literature and critical thinking is all about prioritizing deep engagement, critical analysis, and real-world connections. It's about cultivating students' ability to think critically about the world around them. As educators, we have the power to shape how our students perceive and interact with the world, and it's our responsibility to equip them with the skills they need to navigate it thoughtfully and analytically.
In the end, the goal is not just to teach literature but to foster a generation of thinkers who can analyze, question, and contribute to society in meaningful ways.
READY TO TRY TEACHING EQ DRIVEN UNITS?
LET’S GO SHOPPING
Life's Blueprint: An ELA Lesson Honoring Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.
Dr. King’s legacy is especially powerful in the ELA classroom: his words, his rhetoric, and the passion with which he speaks them is not only worthy of study in its own right, but the overlaps into our content area make the analysis of the layers of his work that much more rich and impactful. Here is a free lesson walkthrough for your middle or high school English class celebrating Martin Luther King Jr.’s birthday.
Life's Blueprint: An ELA Lesson Honoring Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.
Dr. King’s legacy is especially powerful in the ELA classroom: his words, his rhetoric, and the passion with which he speaks them is not only worthy of study in its own right, but the overlaps into our content area make the analysis of the layers of his work that much more rich and impactful.
If your experience is anything like mine, I found myself a bit stuck in trying to find something different to read and analyze in honor of his birthday. By the time students got to me, they had already read or worked through “Letter from Birmingham Jail” and “I Have a Dream”, so a few years back I set out to find another great work to study that would be fresh for students and give them a new angle and understanding of the breadth of Dr. King's work.
What's your life blueprint?
This speech is a fantastic option if you find yourself in a similar position. Take a listen below:
I created a sketchnotes activity for you to use with some other lesson plan suggestions. I'm passing that along to you as just a thank you for being here and because sharing this work is so very important and I don't want anything to stand in the way of getting it done! On a seasonal note, this is the perfect e-learning lesson if school is called off around a snowy or brutally cold MLK day (it’s happened in Chicago before!).
LISTENING WITH SKETCHNOTES
The art of the sketchnote listening activity is that it takes us away from the “fill in the blank” mentality. With sketchnotes, students can actively listen, doodle, draw, sketch, and write in a way that vibes best with their brain’s pace and what emotionally resonates with them. You can play and pause the speech for each number to give students a chance to catch up, to share out loud, or to turn and talk to a partner. It’s important to note that each of the numbered components is NOT a question, rather, they’re phrases from the speech that serve to help students see the outline of his claim at a glance. The space on the page is for them to fill in with the details, evidence, and other words that exemplify that particular portion of the speech.
COMING BACK TOGETHER
Maybe students were turning and talking at a few moments during the speech, but if they haven’t checked in yet, give them that chance. Let them process in a small group table or in pairs through each of the three components of the speech.
Next, create an opportunity for full class discussion. I like to set up a post-it note gallery walk. I place these posters at the center or top of a giant post it note. Then, students move around the room to each of these pull quote posters to:
share a connection
add on to the idea
illustrate how this looks in their mind
elaborate with more detail
When the timer goes off (4-5 minutes is sufficient), students rotate to the next pull quote poster to add their thoughts. As they move, they can bring their sketchnotes with them to reference as they think through the speech with a larger context.
Finally, once students have rotated through each of the posters, you are set up to lead a large group discussion poster-by-poster soliciting students to share their contributions and discuss the speech even further.
GETTING STARTED
I set this lesson up and made the sketchnotes for you already! All you need to do is download them below.
THE IMPORTANCE OF BIPOC LEADERSHIP
The MLK Jr. holiday shouldn’t be the first time that a person of color is celebrated, highlighted, or studied. In the North American calendar, Dr. King’s birthday falls in January, and if we’ve gone an entire semester without looking at non-white leaders and cultural icons, that’s something important to reflect on.
There are opportunities all the time to give students access to meeting and researching the lives of powerful Black American “Influencers”. Before social media culture, activists, leaders, and speakers in the Black community were working tirelessly to shape the cultural landscape of America. Here is one way that I like to do that:
I hope you found these ideas helpful and inspiring. I hope you have a wonderful week at school and happy teaching!
LET’S GO SHOPPING
Planning a Novel Unit Reading Calendar
The art of pacing out the reading during a novel unit can be tricky, so we’re going to take some time today to talk through the process. Whether you’re teaching a classic or a contemporary YA title, there are special considerations to be made for the design of your calendar and how we backwards plan for ELA. Let’s jump in!
Planning a Novel Unit Reading Calendar
The art of pacing out the reading during a novel unit can be tricky, so we’re going to take some time today to talk through the process. Whether you’re teaching a classic or a contemporary YA title, there are special considerations to be made for the design of your calendar and how we backwards plan for ELA. Let’s jump in!
For a while now, I've had the pleasure of guiding countless teachers through the intricacies of curriculum design and instructional coaching. In one of our most recent videos, I delved into a topic that's crucial for any literature teacher: creating an effective reading calendar. Today, I want to share with you the insights and strategies I discussed for building a reading calendar specifically tailored to the novel Fahrenheit 451. You can skim through this post to see the gist and then watch the full video when you’re ready!
Understanding Your Timeframe
The first step in crafting a reading calendar is to get a clear picture of the real time you have available for the unit. It's not just about the number of days on the calendar; it's about the actual class time you can dedicate to reading, discussions, and assessments. This understanding is foundational because it shapes how you'll pace the novel and plan your activities.
Setting Clear Assessment Goals
Before you dive into the reading schedule, it's essential to set your assessment goals. What do you want your students to achieve by the end of the unit? How will you measure their understanding and engagement with the text? These goals will guide you in structuring your calendar and ensuring that each activity aligns with your objectives.
Structuring for Engagement and Ownership
A well-structured reading calendar does more than just outline what to read and when; it fosters student ownership and engagement with the text. I advocate for backward planning, which means starting with your end goals and working backward to determine the steps needed to get there. This approach ensures that every part of your calendar is purposeful and directed towards your learning outcomes.
Decentering the Text for Broader Discussions
In our discussion, I emphasized the importance of decentering the text to allow for broader analysis and discussions. This means assigning larger chunks of reading at a time and not getting bogged down by focusing solely on the text itself, and instead, focusing on the essential question. By doing so, you create space for students to connect the novel to larger themes and ideas, which enriches their learning experience.
A Week in the Life of a Reading Calendar
PIN ME!
Let me give you a glimpse into how I structure a reading calendar. Mondays are for assigning reading, which sets the tone for the week. Tuesdays are reserved for small group activities, which encourage collaboration and deeper understanding. Wednesdays and Thursdays are perfect for close reading exercises, allowing students to dive into the text's nuances. This structure balances guidance with autonomy, giving students the framework they need while empowering them to take charge of their reading.
Flexibility and Adaptation
One of the most important lessons I've learned is the value of flexibility. Every classroom is different, and what works for one may not work for another. It's okay to adjust the reading schedule based on your school's timetable and to be open to rearranging assessment, small group, and close reading days as needed.
Final Thoughts
Creating a reading calendar for Fahrenheit 451 or any novel is a balancing act between structure and flexibility. It requires an understanding of your timeframe, clear assessment goals, and a willingness to adapt to your students' needs. I encourage you to use the template I've provided as a starting point and to check the description box for additional resources.
I wish you all the best in planning your reading calendar. Happy teaching!
LET’S GO SHOPPING
Does Taylor Swift have a place in the ELA Classroom?
And here's the thing: if your students are talking about Taylor, then so should you. This is an open door into engagement and skill building that is not to be missed. Here are three ways to pull the power of Taylor into your classroom and spike engagement among your students…
Well, let's get this out in the open: I'm NOT a Swiftie. I hope we can still be friends, but Tay Tay doesn't have a hold on me in pure Swiftie fashion. To be clear, I'm also not a hater. I'd call myself “Taylor-Neutral”.
Whether you are a die-hard fan or completely out of the scope of Swiftie life, it's impossible to ignore the continually rising wave of her cultural power. Named 2023's Person of the Year by TIME Magazine, Taylor has more than earned her spot in a national conversation – and I bet you she's part of many conversations in your classroom.
And here's the thing: if your students are talking about Taylor, then so should you. This is an open door into engagement and skill building that is not to be missed.
In some ELA teacher circles, I see a hesitation to bring the world of pop culture into our sacred space of literature and critical thinking, but here’s the thing: pop culture and trending icons of the moment are vital tools in getting our students to cross that bridge from their worlds into the deep thought and skill practice that we want so much for them. It may be Taylor today, but keep your eye on other trends that can work in a similar fashion: to create a connection and start a deeper conversation.
Here are three ways to pull the power of Taylor into your classroom and spike engagement among your students:
I already LOVED teaching my annual Person of the Year assignment, but holy smokes, this year will lead to some exciting debate. Did Beyonce get the honor a few years ago? Nope. Did Taylor? She sure did. Last year's award went to the President of Ukraine as a war raged on, and this year's award goes to Taylor…as the world continues to fall apart.
The conversations and writing possibilities around this assignment are endless, but perhaps the most interesting conversation I've ever had with students was determining the criterion for “Person of the Year”. How can a pop icon win it one year, but political leaders earn it in another? What should be considered when choosing the “Person of the Year”?
Taylor Swift's commencement address at New York University has been a favorite of teachers for a long time. This assignment is a highly engaging way to get students to practice their rhetorical analysis skills and break down Swift's approach in sending off a class of graduating students. It’s inspirational for our high school students to envision this stage of their lives - whether or not students are college-bound. The speech is about moving into adulthood and holding firm to one’s identity - a message that will resonate with all students.
This lesson is wonderful to do as an introduction to rhetorical analysis (although it is a bit longer than I’d like — I suggest cutting it a bit) or to use independently as students are reviewing what they’ve learned about SPACE CAT and rhetorical analysis.
Here's what one teacher had to say about this lesson:
“My students LOVED this activity and had some really rich, analytical discussions as a result. I did end up modifying some questions, but this resource was invaluable. The kids were super engaged because Taylor Swift is either super loved or super hated.”
— Elizabeth E
If either of those two ideas aren't what you need right now, maybe this podcast episode will give you the inspiration you're looking for. A few months ago, I had the delight of collaborating on a Taylor-Made episode of The Spark Creativity Podcast. In the episode, I share an idea for using my rhetorical triangle graphic organizer with some of her songs for a quick and engaging lesson. Many more fabulous ELA authors contributed, so make sure to give it a listen!
I hope you've got some ideas now to capitalize on the Taylor energy that seems to always be around. Have a wonderful week at school!
LET’S GO SHOPPING
5 Ways to Look at the Magic of Clarisse in your Fahrenheit 451 Unit
Now, more than ever, we need to have Fahrenheit 451 in front of our students. From the new onset of AI technology to the daily threats of our intellectual and academic freedom, Fahrenheit provides windows, mirrors, and doors into our present and our future. While Montag’s transformation, the working symbolism, and general dystopian world-building are all incredibly important pieces to focus on, I’d like to argue that it’s possible we need Clarisse McClellan the most.
Now, more than ever, we need to have Fahrenheit 451 in front of our students. From the new onset of AI technology to the daily threats of our intellectual and academic freedom, Fahrenheit provides windows, mirrors, and doors into our present and our future. While Montag’s transformation, the working symbolism, and general dystopian world-building are all incredibly important pieces to focus on, I’d like to argue that it’s possible we need Clarisse McClellan the most.
Clarisse.
The enigma.
The one character my students always feel collective sorrow for losing.
She brings us so much in this story but in the chaos of teaching and planning, her magic can be looked over. I’m here to help! Here are the most powerful places to let Clarisse step into the moonlight (too cheesy?):
SKILLS: CHARACTERIZATION - FOIL AND/OR STATIC
One of the very first close reading lessons that we do is a side-by-side close reading between the first introduction of Montag and the first introduction of Clarisse. Between the imagery drawn from nature to the colors used in their description, this is a great place to clearly teach the purpose of a foil or static character. Clarisse’s constancy — her unwavering commitment to being exactly who she is and refusing to conform — is what allows us to see Montag’s transformation. There is a distinct “Montag before Clarisse” and “Montag after Clarisse”. Not all literature gives us such a clear angle to teach this piece of literary craft and I highly recommend using close reading to do this.
SKILLS: FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE - SYMBOLISM
Clarisse is nature. She is water. She is the dew drops on the grass. She is the wind. As we learn about symbolism and track it throughout the novel, Clarisse’s symbols connect our readers to hope and humanity. Clarisse's appreciation for the natural world and her desire to connect with it on a personal level stand in stark contrast to the technology-obsessed, disconnected world of the novel. Clarisse (and her many objects) are a symbol of hope and resistance against a dystopian society. Her existence and actions inspire the protagonist Montag, and by extension, readers, to consider the possibility of change and a better future.
THEMES: HUMAN CONNECTION
If you’ve ever looked around your classroom, I bet you’ve seen phones peeking out of hoodie pockets, fingers flipping through TikTok, and wondered: what on Earth does the future have in store for us? Clarisse is our character to bring everyone back to our humanity (while Mildred does a fine job of warning students of the consequences of continued obsessive technology behavior). Clarisse seeks genuine human connections and meaningful conversations in a world where people are more interested in mindless entertainment and shallow interactions through screens. Her character highlights the importance of real, face-to-face relationships, and every year that I’ve taught this, students DO connect to her. Students DO express the feeling that they’d much rather a world full of Clarisses than a world full of Mildreds.
All of the contrast provided by Clarisse gives us ample opportunity to close read and discuss the roles of other characters. When we look at the Montag and Mildred’s marriage, it is one thing by itself, and an entirely different thing when we consider Clarisse’s impact. Beatty and Montag also have a distinct relationship, and that is shifted entirely as Clarisee’s impact works its way between them.
THEMES: INDIVIDUALITY & QUIET REBELLION
In my Fahrenheit 451 unit, we examine the Essential Question: To what extent is rebellion a requirement for society to progress? Again, Montag typically sits at the center of this conversation, but none of his transformation would be possible without Clarisse. Clarisse values her individuality and refuses to conform to the mindless consumerism and thoughtlessness of her society. Her character serves as a reminder of the importance of maintaining one's unique identity in the face of societal pressures - something that is becoming increasingly harder to do for us as adults and especially for students. She thinks deeply and critically about the world around her. She questions the conformity and superficiality of her society, encouraging readers to do the same in their own lives. Her love for books and the ideas they contain represents a rebellion against a society that burns books to control information and thought. This underscores the importance of literature and the free exchange of ideas.
THEMES: THE POWER OF FEAR
Clarisse might be the first person that Montag has ever heard ask a question, much less questioning authority. She challenges the oppressive government and the censorship of books - and in doing so, is killed. The cost of her quiet rebellion, the cost of keeping the lights on, having conversations, and asking questions…the cost was her life. This underscores the power of fear: when we are afraid of what we don’t understand, fear can convince us to take extreme action in an effort to protect our comfort zone. This might be one of the most important themes for students to take away from studying the novel. Clarisse made Montag uncomfortable, but she also brought him out of the dark and into the light. As we work through Beatty’s speech in Part 1, I like to ask students what Clarisse’s reaction would be to what Beatty is reporting. In so many of Montag’s major close reading moments (moments of transformation), his last trailing thought always comes back to Clarisse and the feeling of her closeness and the painful reality of her loss.
Ready to go all-in on Fahrenheit?
If you’re ready to take the leap and transform the way you’ve always taught Fahrenheit or start teaching it for the first time, I have you covered. My complete unit is designed to take you through 5-6 weeks of inquiry driven, student-centered learning. Learn more about the unit here and be sure to click PREVIEW to take a look inside!
RHETORICAL ANALYSIS RESOURCES
20 Speeches and Text for Introducing SPACE CAT and Rhetorical Analysis
During the introductory phases of teaching rhetorical analysis, you need to start off with texts that are approachable and teachable. This helps to build student confidence as the texts get harder and harder each year. Here are 20 places where you can start that journey confidently!
When it comes to introducing rhetorical analysis for the first time, choosing texts can feel like an intimidating task. But before you get bogged down with which text to pick, let’s talk through a few initial steps to help ensure your success.
TIP #1: Begin with a Framework
When I first was told to “teach rhetoric”, I had virtually no training or support. I resorted to what I knew from my undergrad: an overview powerpoint about ethos, pathos, and logos. This is exactly the path that I would actively AVOID if at all possible (I’ve written about that more here), and instead begin by introducing students to the framework that you’ll use in order to do the work of analysis. For me, I’ve found SPACE CAT to be my favorite ( BTW, I also do this with poetry using The Big 6).
TIP #2: SKIP ETHOS, PATHOS, LOGOS IN YOUR INTRO
Okay — hear me out. I’m not saying don’t teach ethos, pathos, or logos. I’m saying don’t use that as an INTRODUCTION to rhetoric.
Here’s why:
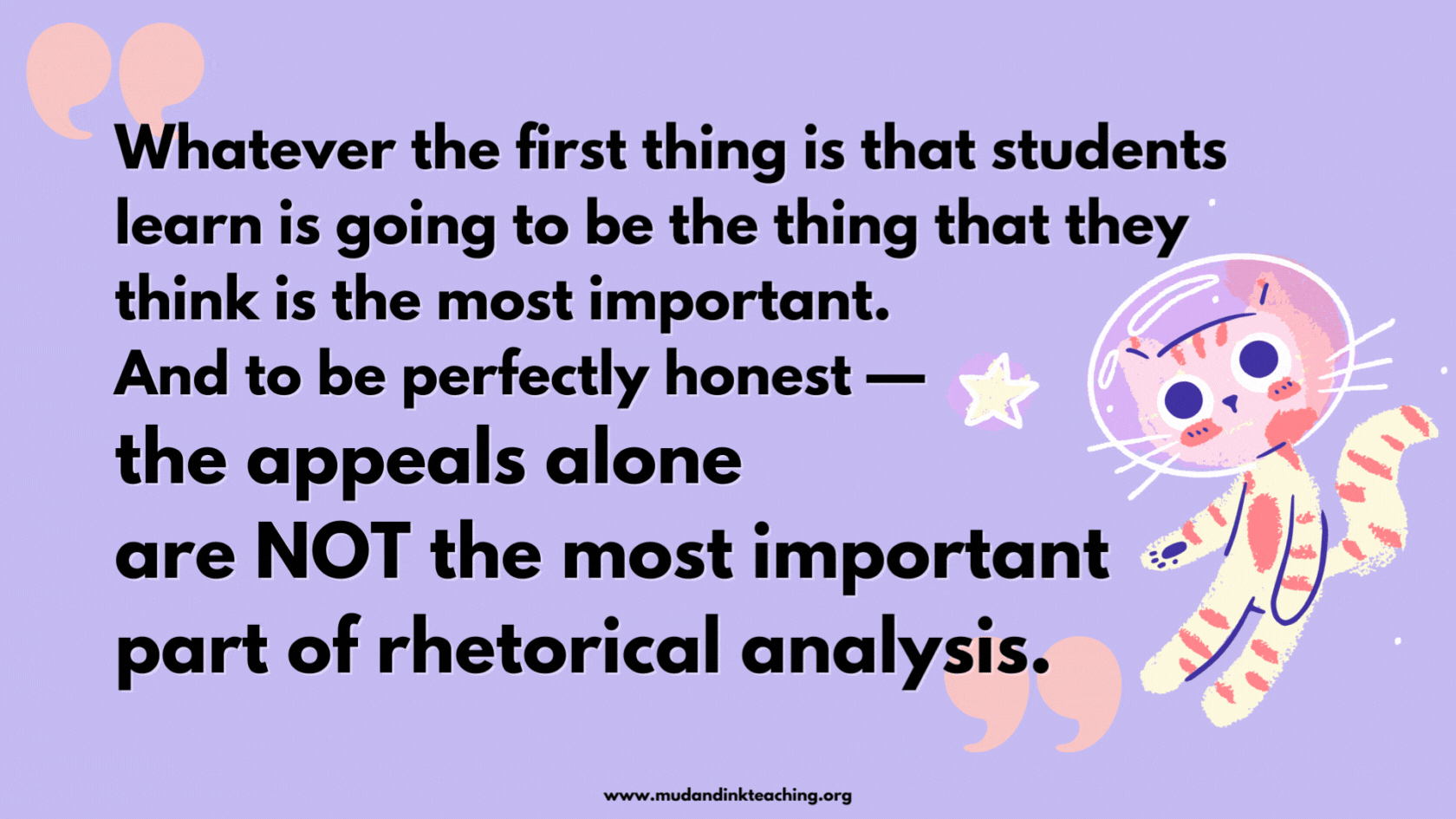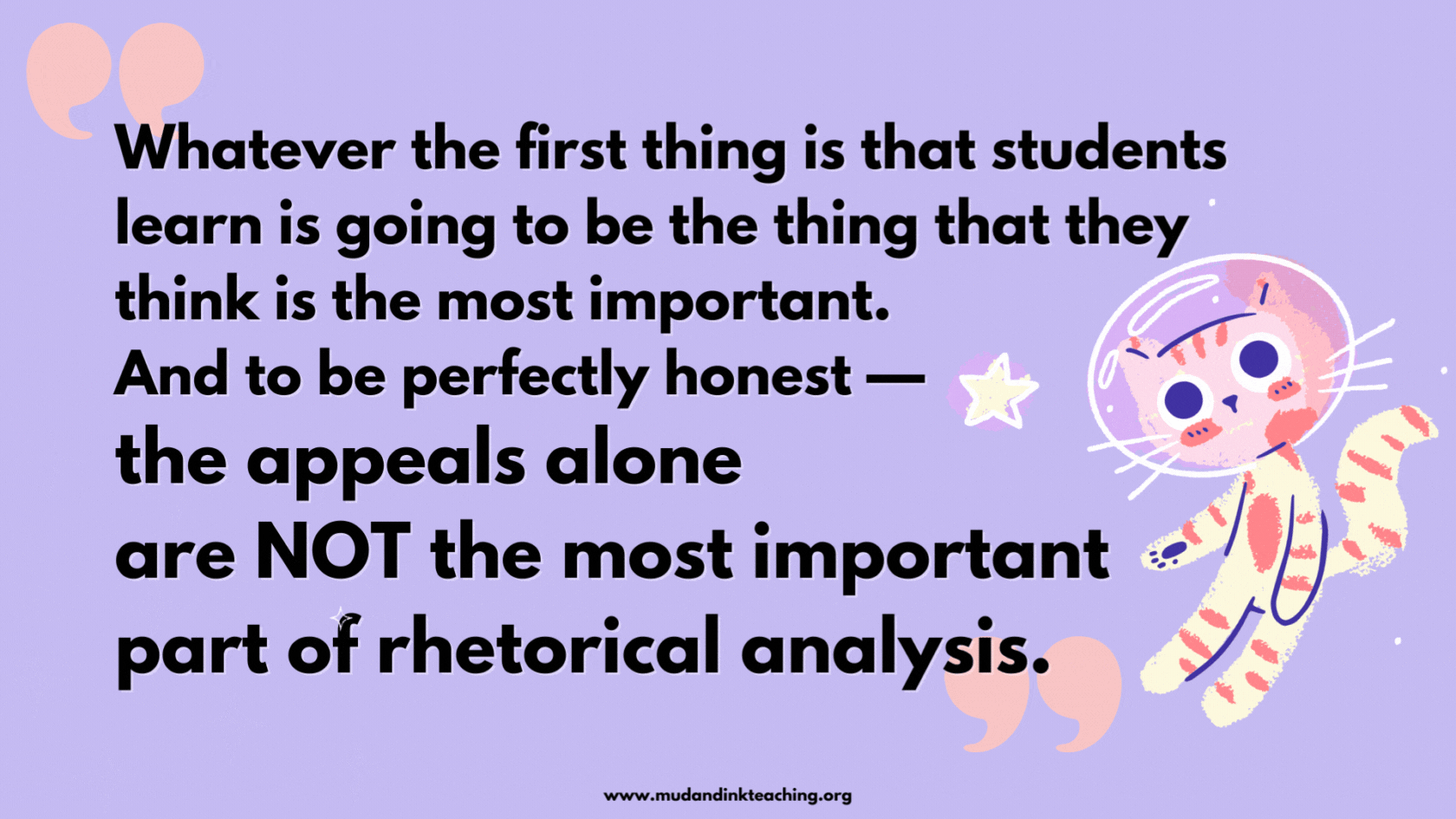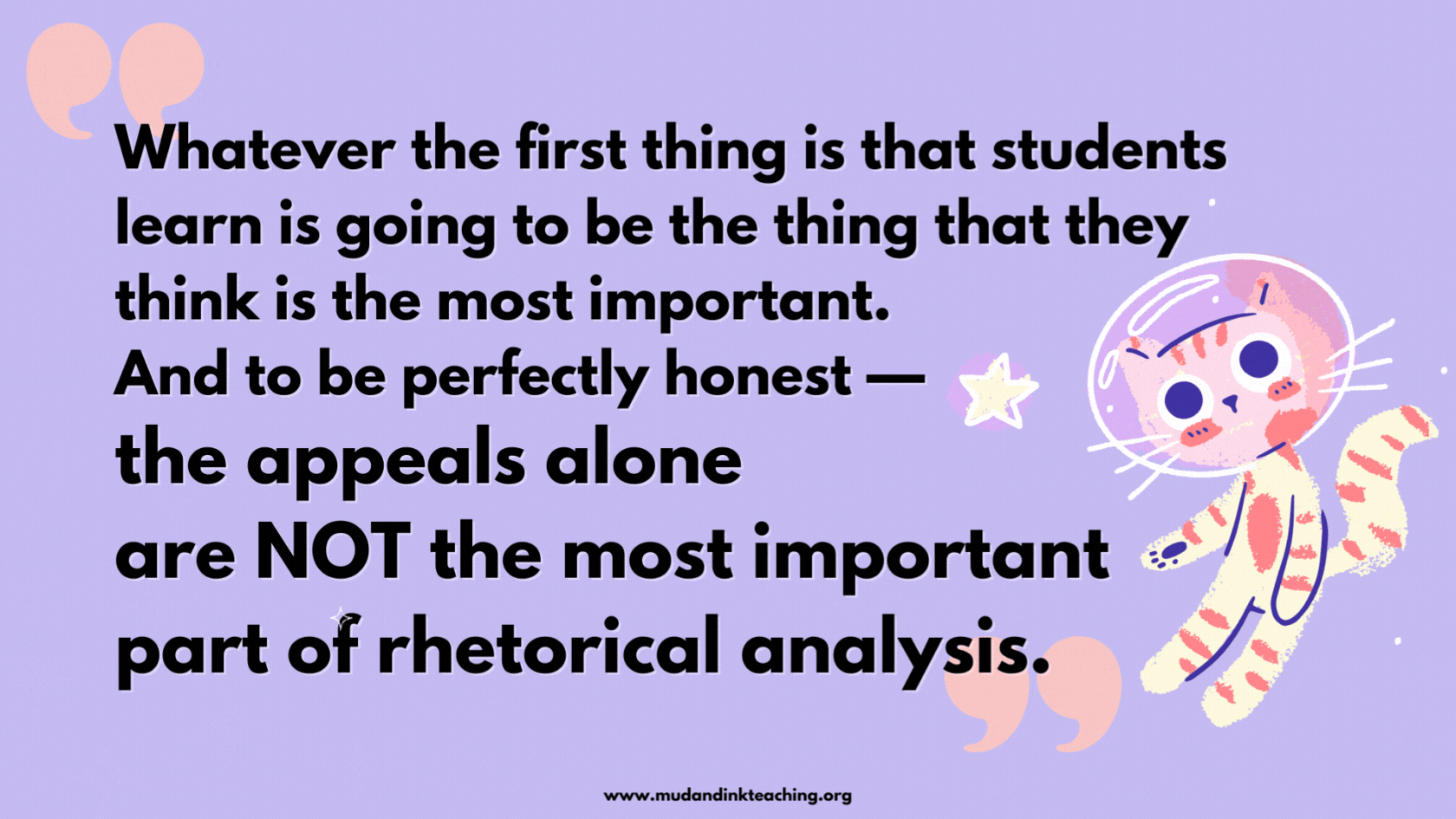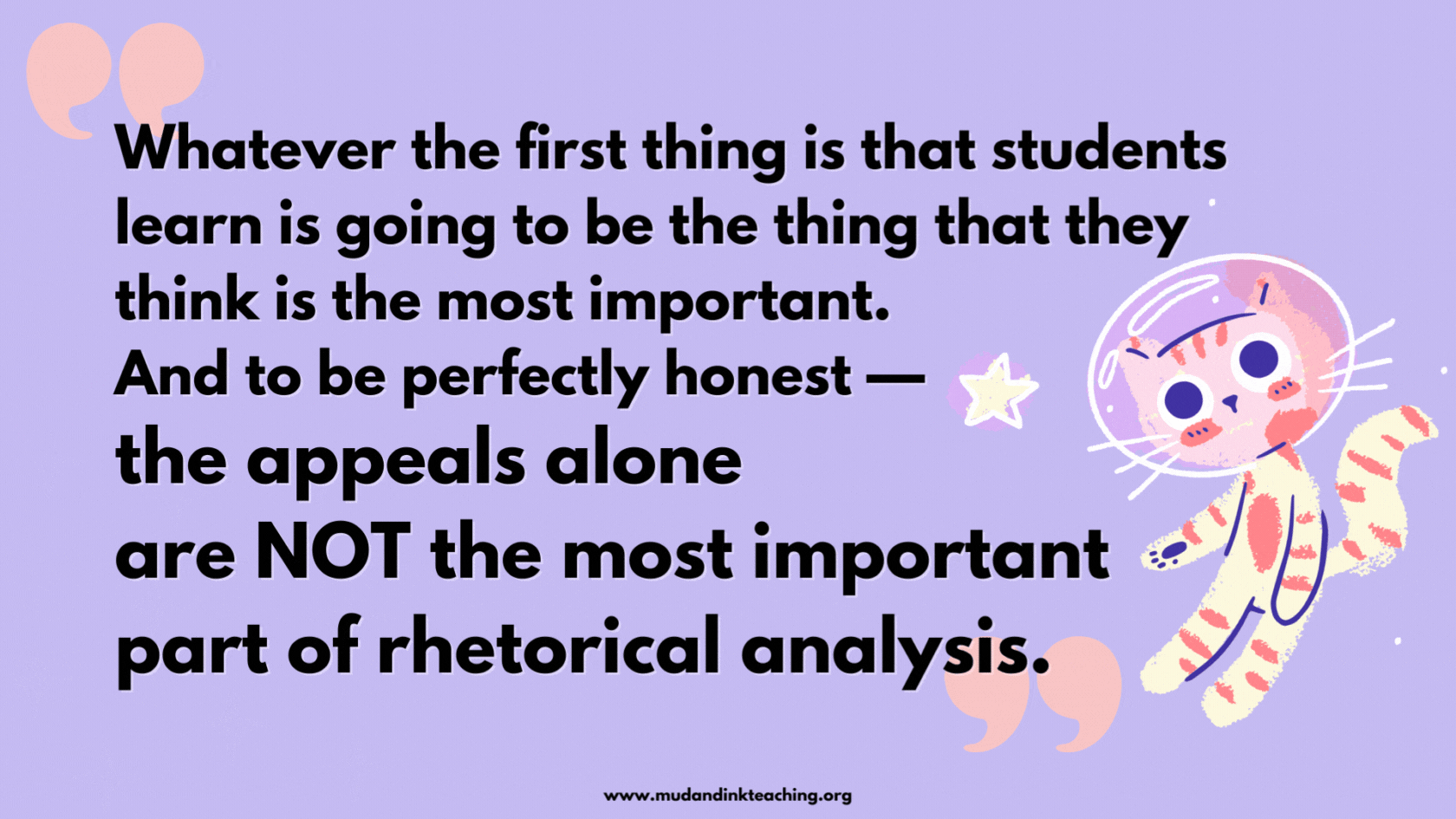
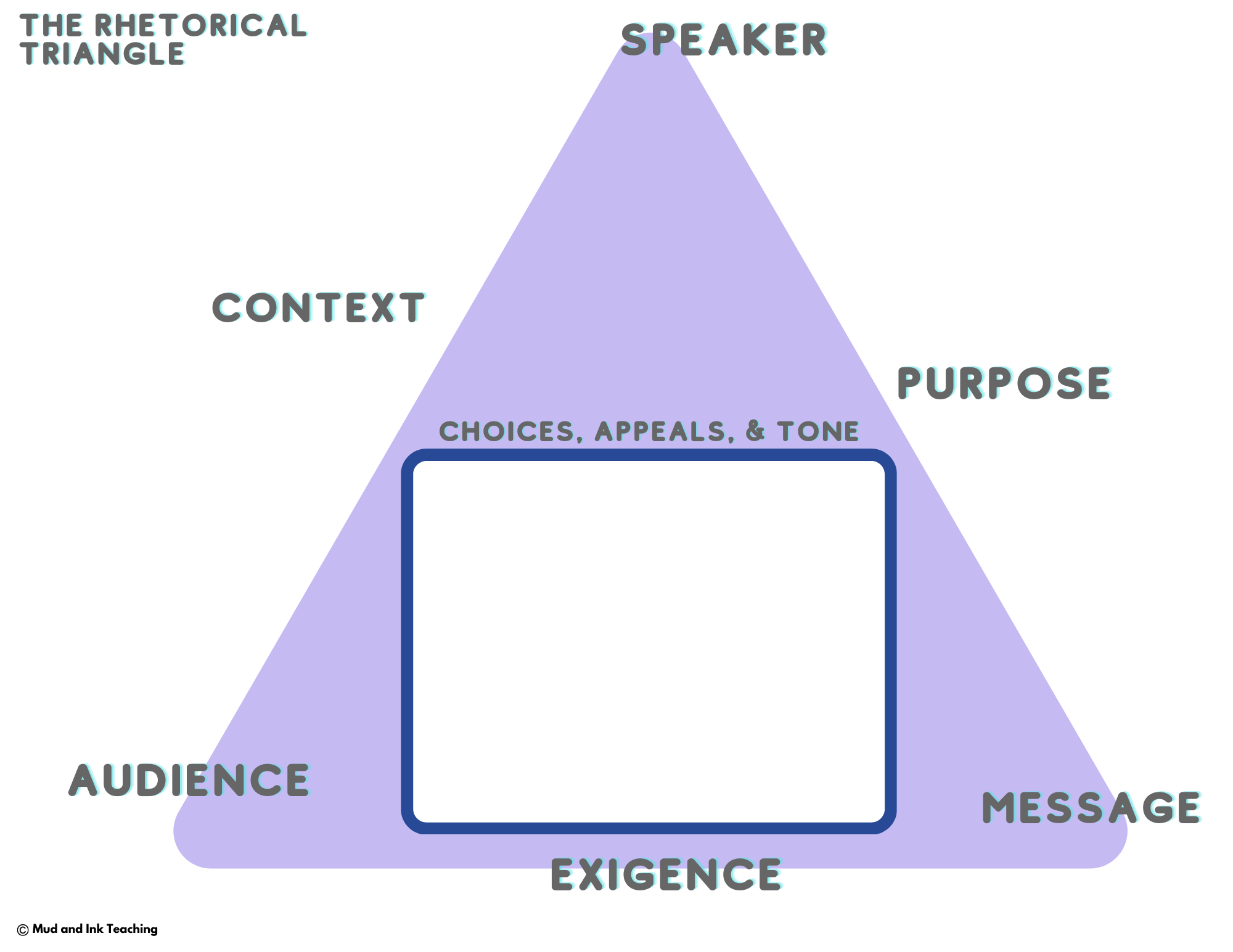
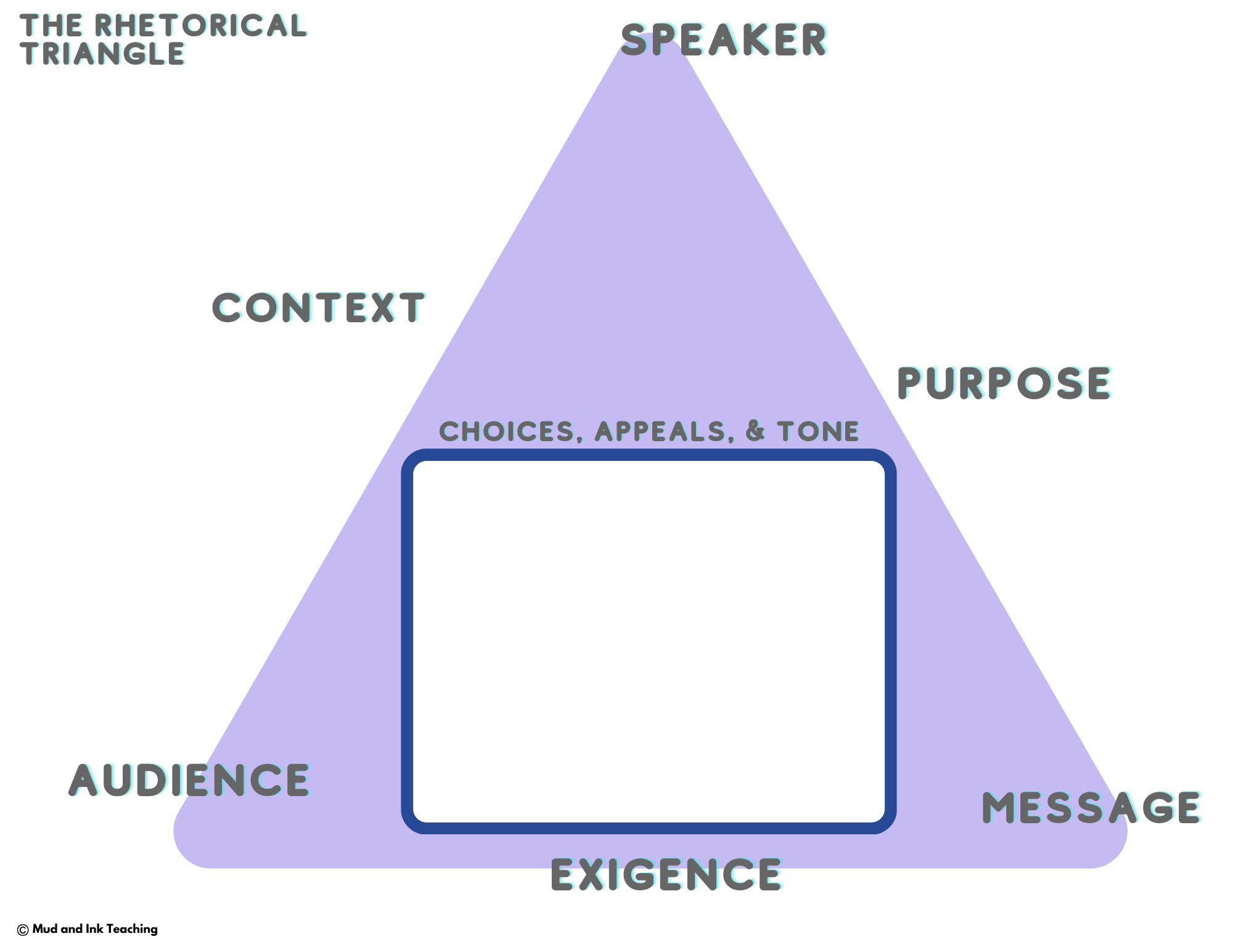
Whatever the first thing is that students learn is going to be the thing that they think is the most important. And to be perfectly honest — the appeals alone are NOT the most important part of rhetorical analysis.
So what to do instead? Introduce the RHETORICAL TRIANGLE.
The Rhetorical Triangle sets students up to see the ways in which an argument moves from one person to another. It centers students on their role as analysts and the need to be inside of the argument - not outside attacking it with a highlighter.
For two more in-depth discussions and lesson examples on the rhetorical triangle, start here:
“Be Our Guest” from Disney’s Beauty and the Beast
“Mother Knows Best” from Disney’s Tangled
TIP #3: TEACH ON REPEAT
If you’ve not started “template teaching” let me encourage you to make this the day that you start. As you browse through the list below, try to think of these texts as opportunities to teach and reteach the same skills over and over — not a daunting list of individual lesson plans.
Begin by introducing the rhetorical triangle and situation using either of the two lessons listed above. During those lessons, introduce students to the rhetorical triangle graphic organizer template and help them become well acquainted. This graphic organizer will be the TEMPLATE to print and repeat for every lesson hereafter.
Once students are ready to move to more challenging texts, start movin’. What’s the lesson? It’s all baked in to your graphic organizer template. Using just that one handout, students can do a huge variety of tasks all with varying levels of challenge and independence. Here are a few ideas:
In small groups, bullet point details about the speaker. SHUFFLE GROUPS, and in the new group, bullet point details about the audience, SHUFFLE GROUPS, and in the new group bullet point details about the context. Repeat as needed for each element of SPACE.
Read/watch the text together. Complete S - P - A together and assign C - E to work on in pairs
Put students in small groups. Designate areas/tables around your room as S, P, A, C, and E. Have students move through each station with their group and their handout to analyze the text.
Have students choose any text from a provided list and complete the graphic organizer independently for homework / individual work
This template allows you to flex the details of your lesson without having to prep brand new handouts for every single new text!
THE LIST YOU’VE BEEN WAITING FOR: THE BEST TEXTS FOR INTRODUCING SPACE CAT
This list comes both from personal experience and teacher recommendations. If you have experience or more ideas, please feel free to add them to the comments at the end of this post!
“The Other Side” from The Greatest Showman
Battle speeches from Queen Magra and Baba Voss from the Apple TV Series See
“Be Prepared” from Disney’s The Lion King
“I’ll Make a Man Out of You” from Disney’s Mulan
“Under the Sea” from Disney’s The Little Mermaid
“How to Mark a Book” by Mortimer Adler
“Farewell to Baseball” Lou Gherig
Challenger Speech from Ronald Reagan (and grab my close reading template for this speech here)
9/11 Address from George W. Bush
“Offensive Play” by Malcolm Gladwell
Back to School Commercials
What would you add to this list? I’d love to hear it in the comments below!
Happy teaching!
RHETORICAL ANALYSIS RESOURCES
55+ Books for Your Next American Dream Unit for High School ELA
One of my favorite units to teach is a unit that focuses on the American Dream. It’s the perfect way to hone in on complex characterization and the layers of complexity are widely accommodating for skill level. Whether you’re building the unit to teach as a whole class novel unit or as a literature circles unit, this book list is here to save you time and energy in narrowing down the search.
THE AMERICAN DREAM: INSPIRING OR DESTRUCTIVE?
One of the most frequently taught units in the American high school system is one centered on The American Dream. In some cases, this can be the focus for an entire 11th grade year study of literature. And while it’s a necessary and important lens for us to use when examining literature, it can get stale or even oversimplified when working with students. After several years of experimenting, I have found this Essential Question approach to excite and engage students across skill levels, interests, and backgrounds. Whether you’re building the unit to teach The Great Gatsby, A Raisin in the Sun, or another American classic or you’re ready to tackle this topic as a literature circle unit, this book list is here to save you time and energy in narrowing down the search. The books on this list open up the conversation about the American Dream widely and represent a variety of experiences and voices.
Themes VS Essential Questions
For a long time, I taught theme-based units: units were based on a teacher’s pre-selected theme and all of the learning was connected underneath the umbrella of the theme. I really liked the sense of connectedness, and quite honestly, I was craving that coming from a much less organized situation when I began my career. But no matter how hard I tried, I couldn’t shake the teacher-centeredness of this approach. The students had very little investment in the choice of the theme, and the direction of the conversation around the theme, and so much of it was tied to the teacher’s decided trajectory for the unit.
Inquiry, on the other hand, gave me the chance to use the best parts of themes, but deepen them and hand them over to students. Inquiry takes a thematic idea, roots it in a question, and then asks students to spend the duration of the unit investigating and exploring potential answers to that question as they progress toward the summative. Look at it this way as a “unit makeover” :
BEFORE: Unit 1: THE AMERICAN DREAM
AFTER: Unit 1: IS THE AMERICAN DREAM MORE LIKELY TO INSPIRE OR DESTROY?
The thematic/topical unit states the focal point of the unit and we can assume that each of the texts in that unit will reveal different versions of the American Dream. The inquiry unit will do those same things as the thematic unit, but nudges students a massive step further: is it more likely to inspire us to do great things or destroy us along the way? The argumentative edge to this question presses students out of simple definitions and into the messy business of stating a claim on a continuum. This one big question begs dozens of smaller ones and sets up a unit that is connected, but also divergent. Most importantly, this question helps the unit address the critical nature of the way the dream manifested in drastically different ways depending on a person’s race, immigration status, and ancestry. This is a unit that is unified under a topic (The American Dream), but also ready to twist and turn with student curiosity. In the video below, I give a big longer take on the ways this question opens up possibilities within a unit:
Scroll through the list below of titles that are absolute perfection for this particular unit. Bookshop.org is a wonderful partner working to bring business to small, local bookstores, so if you can swing it, shop the list directly and you’ll be able to help out bookstores in your area!
Elevating Your Gatsby Unit: Examining Inspiration and Destruction
The duality of the American Dream - its capacity to both inspire and destroy - lies at the core of F. Scott Fitzgerald's iconic novel, The Great Gatsby. When teaching this masterpiece, the essential question, "Is the American Dream more likely to inspire or destroy?" serves as a powerful lens through which students can explore the complex and often contradictory nature of this elusive ideal.
Through Gatsby's relentless pursuit of his dream, students witness the transformative power of ambition and hope. Yet, as his story unfolds, they also grapple with the destructive consequences of his obsession, the moral compromises he makes, and the ultimate emptiness of his achievements. This essential question allows students to delve into the multifaceted aspects of the American Dream as portrayed in the novel, from the glittering allure of wealth and social status to the disillusionment and despair that can lurk beneath the surface.
By incorporating this inquiry-driven approach, teachers can foster a more dynamic and engaging learning environment. Students are encouraged to question and analyze the various characters' journeys, their motivations, and the ultimate consequences of their pursuit of the American Dream. This leads to rich discussions, insightful writing, and a deeper appreciation of the enduring relevance of Fitzgerald's cautionary tale.
SHARE IN THE COMMENTS!
What other books would you add to this list? I know there are so many that fit this EQ so perfectly and it was hard to keep the list manageable. I’d love to hear your additions in the comments!
let’s go shopping!
Teaching Short Story Units with a Modern, Contemporary Twist in Secondary ELA
If you’ve ever found yourself searching the internet for “contemporary short stories” or “modern short stories” because you’re tired of teaching the same classic stories over and over again, I have THE HACK to change everything for you!
If you’ve ever found yourself searching the internet for “contemporary short stories” or “modern short stories” because you’re tired of teaching the same classic stories over and over again, I have THE HACK to change everything for you!
I won’t even make you wait until later to hear my little secret. I’m just gonna spill the beans :)
Stop searching for short stories and start teaching NOVEL EXCERPTS!
THE BENEFITS OF USING NOVEL EXCERPTS
Let’s get something clear from the get-go. This blog post is not advocating for exclusively teaching excerpts all year long. Some context here is very important: my suggestion is to use novel excerpts to update the outdated short stories that we find anthologized so frequently. This is a suggestion for the teacher in a short story unit rut that wants more voices, more styles of writing, and something that’s both easily accessible and FREE. Almost all of our favorite YA and adult novels have sample chapters available online, oftentimes directly from the publisher’s website.
All this is to say, we NEED full-length works in our curriculums. But that is a blog post for another day and not what you came here for. So let’s proceed.
DIVERSE VOICES
When we talk about the kinds of texts our students need, the conversation should always come back to representation. Are the life experiences, family dynamics. racial histories, gender identities, and other ways that make our students’ lives unique and important need to show up in the stories and protagonists that we include in our curriculum. Using publisher’s websites and Goodreads is a great way to research titles for the voices that you think your short story unit is missing. Once you’ve found a title, search the novel title and the word “sample” or “excerpt” in Google, and more likely than not, you’ll come up with a result!
Not all excerpts are created equal, of course, so read through what you’ve got and make a call.
Need more insight on representation and our classroom libraries? Check out this guest post from my friend John Rodney about inclusive LGBTQ+ stories and protagonists.
2. VARIED WRITING STYLES & GENRES
Here is another thing that is easier to search with novels as opposed to short stories: searching by genre! So often I see teachers lumping a bunch of stories together and naming their unit the “short story unit”. In this case, all that the stories have in common is that they’re, um, short? Not novels? So thinking through the idea of genre, not only can we find stories with general commonalities, but it sets us up nicely the opportunity to build Essential Questions.
3. FREE, HIGH-QUALITY TEXTS
I love book shopping just as much as the next English teacher, but when it comes to picking up anthologies, skimming the table of contents, and then reading each and every story, it can become a cumbersome task when rewriting a unit. Is it worth it? Absolutely — but only if you have the time and the budget. If you’re out of time and have zero budget, follow the tips above and start with your favorite novels that you think speak to each other. Start layering your excerpts underneath the umbrella of an Essential Question until you have a rich, varied, interesting, and most importantly, FREE brand new set of texts.
TWO SHORT STORY-EXCERPT UNITS TO TRY
If the above info was enough for you to take this idea and run with it, by all means, go and run! But if you’re wishing that you had a model to look at before getting started, I have two units to share with you here. I’m happy to share the gist and outline with you here, and if you’d like to purchase either, they’re only $8 each in my TpT store.
START WITH YOUR ESSENTIAL QUESTION
To me, this is the most vital part of the short story unit makeover. Units that are driven by inquiry and curiosity beyond the texts provided create a natural engagement that’s hard to achieve otherwise. So here are two EQs that I’ve used with short story units:
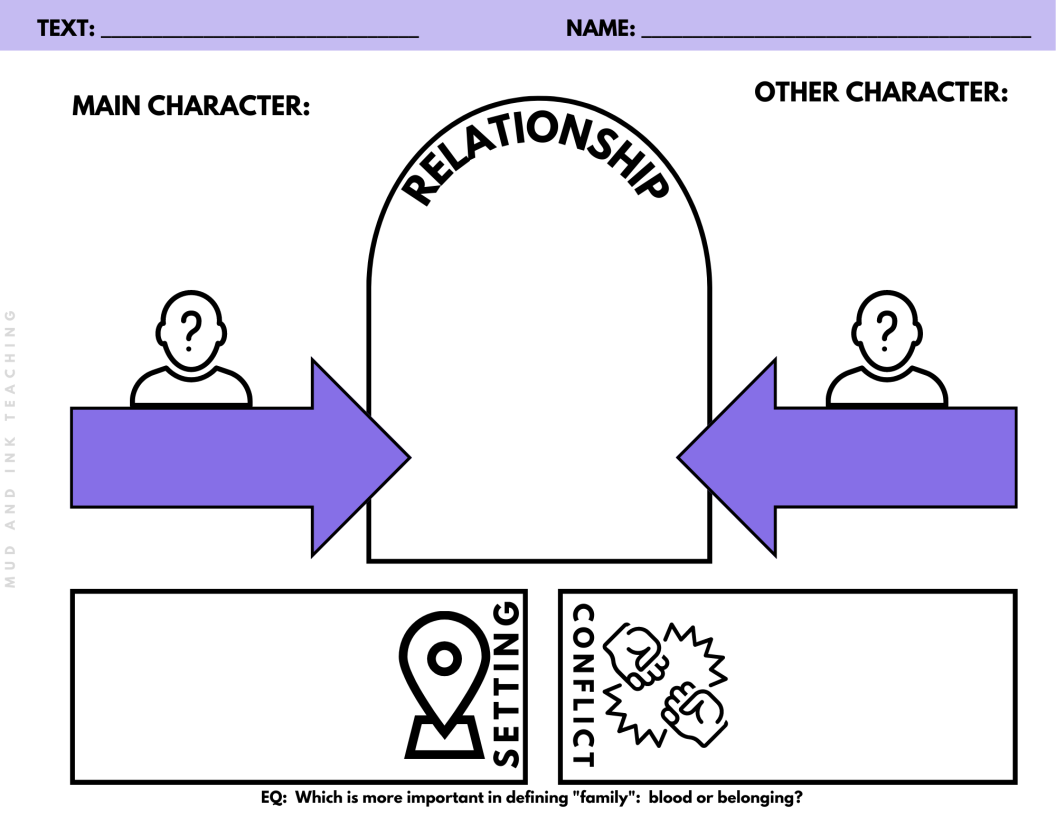
Which is more important in defining "family": blood or belonging?
Through which lens is it better to view others: trust or skepticism?
Each of these questions sets up an interesting task for the creator (you!). What kinds of voices can I find to shed light on this question? What are the various branches that lead back to this EQ? How can I share a variety of perspectives and experiences across time, gender, race, ethnicity, and genre? Or even — would one of these questions set me up to explore various ways of exploring one genre?
BUILD YOUR TEXT SET
So for the first question about family, I decided to treat this text set thematically: each text will offer a different perspective on the idea of what makes a family a “family”. I started with a few novels that came to mind right off the bat: Where the Crawdads Sing by Delia Owens, Far From the Tree, and . To find a few more, I went to Goodreads and searched “family”. After reading a few summaries and checking out their corresponding excerpts, I decided that Take Me With You When You Go by David Levithan and Jennifer Nevin and From Here by Luma Mufleh would be a perfect fit. This grouping offers us fiction, memoir, multiple narrator style storytelling, a novel in verse, a story about pregnancy and adoption, a refugee perspective, and so much more. No matter how different and varied these stories are, they all come back to the same thread: how do we define family?
For my other question, I had in mind a mystery and suspense genre focus even before writing the EQ, so I knew I wanted to have the texts be connected by genre. I pulled a few thrillers, a few mysteries, and was sure to include a YA crowd favorite: One of Us is Lying. My complete text set list includes excerpts from:
One of Us is Lying by Karen M. McManus
Monday’s Not Coming by Tiffany D. Jackson
The Box in the Woods by Maureen Johnson
In a Dark, Dark Wood by Ruth Ware
The goal of this particular unit is to give students the opportunity to explore the genre of mystery and thriller while trying to find out what these kinds of stories tell us about how we should approach our own view of the world.
BACKWARDS PLAN YOUR UNIT
With short stories, it’s important to backwards plan the same way we backwards plan any other unit. Here are a few questions to ask yourself as you sit down with your planner (I use Artful Agenda: a pretty, digital planner that syncs up with my Google Calendar):
What is your goal for this unit?
What should students be able to do by the end of this unit?
What assessment tool will be used to measure students at the end of the unit?
What can I use regularly during this unit to give students plenty of practice?
Which skills need direct instruction and which need review and practice?
The true danger of any unit is trying to plan starting with day one and forgetting about the end until you get there. Short stories can take a surprisingly long time to read and discuss, so by backwards planning, you can avoid being blindsided by your own story selections (I’ve been there — “The Lottery” and I have a long history of ups and downs). In my short story units, I plan backwards using templates (similary types of lessons on repeat). Every unit I teach must have:
A gateway activity (something to spark curiosity and get them excited about the EQ)
An anchor tool (a graphic organizer or handout that is used on EVERY short story to help students focus on the most important skills of the unit)
Formative assessments
Summative assessment
From that starting point, I begin to fill things in little by little keeping in mind the realistic pace that I’d like the unit to have.
MORE SHORT STORY UNIT IDEAS
My co-host of the Brave New Teaching podcast, Marie Morris, has a wonderful short story unit that’s entirely made up of folktales and fairy tales. She walks through the unit in this episode here:
Are you excited about the idea of threading together your short story unit with Essential Questions? I have an entire blog post dedicated to even more ideas for EQs and text set suggestions. Check it out here!
LET’S GO SHOPPING!
How to Create Book Club Magic Using Essential Questions {Part Two}
Lackluster literature circles? Boring book clubs? The remedy: lose traditional “role” sheets, declare freedom from organization by topic or genre, and build essential question-focused literature circles or book clubs instead. An EQ as the throughline for your lit circle/book club unit kicks up the impact that comes from having kids talk about what they read in a way that just does not happen with any other method. Here’s why…
Lackluster literature circles? Boring book clubs? The remedy: lose traditional “role” sheets, declare freedom from organization by topic or genre, and build essential question-focused literature circles or book clubs instead. An EQ as the throughline for your lit circle/book club unit kicks up the impact that comes from having kids talk about what they read in a way that just does not happen with any other method.
This is the second blog post in a series dedicated to this kind of magic. Make sure you catch Part One when you finish reading here!
REASON # 3 – BUILD COMMUNITIES WITHIN A COMMUNITY
Lit circles like “real” life book clubs
One of the great things about lit circles and book clubs is how they build communities within your larger classroom community.
In “real” life, we join book clubs to find community – to have a social outlet where we share a common interest. And even though lit circles have always had a cooperative learning element built in by design, using an EQ focus takes it beyond a learning strategy.
First, kids choose their book in a more authentic way, so regardless of how well they might know other students in their group, they have an immediate connection.
Second, like in “real life” book clubs where discussion is not dictated by a “role” but with genuine questions, connections, and a desire to understand, an EQ provides a touchpoint for question creation and passage selection. It also offers a way for groups to come back to center and ground discussions if focus waivers.
The work with supplementals and text pairings also offers students opportunities to build community as they try to make connections and develop understanding between texts, looking at “big” ideas through different lenses. Jigsawing between groups is a community builder, and EQs offer more opportunities for this because the text is not centered.
An EQ offers the opportunity for students to easily connect digitally. With no shortage of apps for virtual meetings, book groups can even be created between classes, providing alternative ways to foster and develop community.
As students share their thinking and debate and consider one another’s ideas, whether it is within their “home” lit circle or during a jigsaw, they learn from each other. They consider new perspectives. They lean on each other to understand and analyze the texts they read, creating a sense of belonging at a different level.
CHECK OUT AMANDA’S FAVORITE BOOKS TO USE IN An AMERICAN DREAM EQ UNIT:
REASON #4 – EASE OF ASSESSMENT
EQ = lit circle/book club assessment special sauce
How to assess students and what to assess them on is an often-cited source of frustration. You are not alone if you’ve worried about any/all of the following:
What if I haven’t read all the books?
How do I keep them accountable individually? As a group?
How do I know if they are reading?
Should there be a group assessment?
Projects? Writing?
But when your book clubs or lit circles are EQ-focused, they are skills-based, not text specific. And an EQ and backwards planning – knowing what your summative will be at the beginning of the unit – develops students’ skills throughout the unit so they can find success.
The focus of assessment, simply put, is to answer the essential question using whatever texts they encounter throughout the unit whether it is their novel, pairings or supplementals. Depending on your skills focus – developing interpretive-level questions, providing strong evidence to support thinking/writing/speaking, connecting concepts across multiple texts, paragraph writing – the summative could be:
a student-run Socratic with student-developed questions
a podcast
an analytical paragraph or essay
a synthesis essay
a one-pager
Throughout the unit, individual and small group check-ins could include:
written reflections
creating discussion questions and choosing passages for each meeting
write-arounds
hexagonal thinking activities
choice-board activities
and Sesame Street quizzes
that focus on the skills students need to practice as they work toward their summative.
EQ-focused book clubs and lit circles, like other EQ-based units, prioritize understandings about life that are bigger than the text/novel alone, making assessment more authentic and simpler to plan using backwards design.
CONCLUSION
EQ-focused lit circles or book clubs, by design, create an authentic, choice and skill-based, rigorous shared reading experience that your students will benefit from and you will enjoy guiding.
What have your experiences with book clubs/lit circles been like as a secondary English teacher? What questions do you have about EQs, backwards design, or EQ Adventure Packs? Let me know in the comments!
Curious about how the thought process goes into an EQ unit? Listen in here to get a feel for how I break down this EQ and the levels of complexity available to teachers and students with just this one question: Why do relationships matter?
Believe it or not, there are even MORE reasons to lean into an EQ-centered appraoch to lit circles, and there’s a PART ONE to this blog series! Did you miss it?
LET’S GO SHOPPING!
Four Review Games & Activities for the AP Lang Exam
Tackle the AP Language and Composition exam with confidence using any of these four classroom-tested review strategies. This list will give you plenty of ways to prepare for the exam while having fun and working hard to get students as ready as possible for test day.
Test prep is a mixed bag of emotions for me. Teaching to any test is a quick trigger of my fury, but after time and experience with the AP Language and Composition exam, I’ve really shifted my mindset. In many ways, the entire course is test prep. The course is backwards designed: exam at the end, curriculum built from back to front to support the skills needed to perform on said exam. But what’s different about the Lang exam than any other test I’ve ever experienced in the secondary education world is that I care about these skills.
Are the timing constraints, blind prompts, and other testing factors perfect? Not by a long-shot, but time after time, I’ve seen my students flourish as writers over the course of a year as they prioritize the skills that show up on the exam.
So here’s the thing: we don’t talk much about the exam during the year. Yes, we do some timed writes, but those are for me to measure progress and less about “prepping” for the exam. But when it gets closer to exam time, we do start to talk more about the components of the exam and discuss the different ways students would benefit from reviewing the coursework and practicing the skills before test day.
These are four of my favorite review activities that I wanted to pass along. I hope you find a few gems here and can take a bit of the workload off your shoulders this May!
Choice BoardS
Not every student needs to work on the same things, and this is where a choice board comes in so incredibly handy. With a choice board, you can create categories of review study and load each category up with options that will review, give practice, or challenge students as they prepare for the exam. I design my choice boards in either Google Slides or Canva. In Slides, I build the board using VIEW —>. TEMPLATE, basically building out the “background” of the slide. Then, I add buttons on top of that background that are clickable and linked to various review materials. In Canva, I make the board, link each box, and then share a VIEW ONLY link with students. It makes no difference at all what you use — it’s all up to your comfort level. I have one made and ready to share if you want to take a peek and see if what I have will work for your students, too.
2. Mother Knows Best (Disney)
When it comes to reviewing for RA, there’s nothing more that I love than using some Disney. Disney songs (and so many other songs in musicals) are plot based, therefore, the characters that are singing often have an agenda of some sort. Take Mother Godel, for instance. After kidnapping the princess to take advantage of her magical hair, Mother Godel has a lot invested in this tower situation. It’s imperative that she keep Rapunzel in that tower locked away, so when Rapunzel starts to get a bit curious and ask questions, Mother Godel shuts down that show pretty darn fast. Using Disney songs and movies are a playful way to review RA skills, and at this time of the year should be pretty easy for students to dive into in small groups without teacher assistance. I also use these to introuce rhetoric, but a Mother Godel lesson in October is a very different from one in May. Use it how it best suits you!
3. Commencement Speeches
There are many benefits to using commencement speeches for exam review:
They fit into the end of the year feel and thematically feel like a natural fit this time of year
Commencement addresses are frequently used on FRQs if you check out past exams
There are plenty of engaging, interesting speakers to choose from all across YouTube
Depending on the speech, you might need to amend the length, but other than that, these speeches are abundant and easy to find. I like to take these speeches and break them up into pieces and make small groups experts on each piece. We then bring the pieces together for a “work as a whole” conversation and that is usually very powerful in preparation for exam day.
A few more speeches I love using:
4. Spare Change Game Show
If you’re looking for a whole class, interactive, hysterical and fun way to practice argument, The Spare Change Gameshow is it. All you need is a coin to flip and a timer! Using my slide deck, students are paired up and face off arguing for and against a wide set of claims. My favorite part of this exercise is that the coin decides the students’ argumentative fate: heads must argue the affirmative, and tails must argue the negative. It makes no difference whether or not they actually agree or disagree with the claim: they must comply with their coin’s decision.
So there you have it, folks. My four favorite ways of exam prep before the AP Lang Exam. I hope one of these resonated with you and that you have a wonderful end of your school year with students. Let me know in the comments how you’re feeling this year and which of these review materials you plan on using!
LET’S GO SHOPPING
How to Create Book Club Magic Using Essential Questions {Part One}
Lackluster literature circles? Boring book clubs? The remedy: lose traditional “role” sheets, declare freedom from organization by topic or genre, and build essential question-focused literature circles or book clubs instead. An EQ as the throughline for your lit circle/book club unit kicks up the impact that comes from having kids talk about what they read in a way that just does not happen with any other method. Here’s why…
Lackluster literature circles? Boring book clubs? The remedy: lose traditional “role” sheets, declare freedom from organization by topic or genre, and build essential question-focused literature circles or book clubs instead. An EQ as the throughline for your lit circle/book club unit kicks up the impact that comes from having kids talk about what they read in a way that just does not happen with any other method. Here’s why:
REASON #1: CHOICE, BUT LIKE, FOR REAL
Fundamental Tenet of Lit Circles and Book Clubs
Fact: choice boosts student engagement. And even in the “passage picker, summarizer, questioner, illustrator” role sheet days of early lit circles, students selected books that most interested them – usually within a specific genre or topic.
Great, right?
Sort of.
What about students who:
detest dystopia?
hate historical fiction?
can’t stand “coming of age”?
They have choice. Among titles they wouldn’t otherwise pick for themselves.😕
When lit circles and book clubs focus on essential questions (more info on essential questions and inquiry-based learning here and here), novel options for students – unbound by any constraints other than shedding light on the question – grow exponentially!
For example, if your book club/lit circle essential question is why do relationships matter? book choices could include:
The Outsiders
The Hunger Games
and The Crossover
or
The House on Mango Street
Long Way Down
and The Children of Blood and Bone.
Classics. Novels in verse. Realistic fiction. Fantasy. Dystopia.
Something for every student's interest and background, and this is just a short list of possibilities for tackling this EQ! The EQ focus makes the book selection more authentic for the kids. Instead of “the least worst option,” their choice becomes something that truly speaks to their personal preferences as readers thereby creating more emotionally engaged lit circle/book club participants who are ready to tackle the EQ!
CHECK OUT AMANDA’S FAVORITE BOOKS TO USE IN A RELATIONSHIPS EQ UNIT:
REASON #2 – RIGOR
EQ-focused lit circles and book clubs elevate rigor!
While choice certainly helps open the door to student engagement, rigor plays a role, too. By rigor, I do NOT mean offering only complex texts, accelerated reading calendars, or piling on assignments.
As high school reading and writing gurus Kelly Gallagher and Penny Kittle say in their latest book, 4 Essential Studies, rigor does not equal text difficulty.
““Book clubs motivate us to read. They deepen our understanding of not only the book but how others read and interpret the same text … rigor is not in the book itself, but in the work the students do to understand it” (45-47). ”
And the work students do with EQ-focused book clubs or lit circles encourages this work.
Sure, in a genre-based book club, the kids can examine what elements show up in their book and how. They can compare how one author achieves this versus another.
But an EQ, like Which is more powerful: hope or fear? immediately asks students to sit with uncertainty and consider possible answers and solutions rather than identify more correct ones.
EQ-based lit circles or book clubs meet students where they are – literal, theoretical or anywhere in between – and provide opportunities to scaffold toward analysis, synthesis and more abstract thinking.
How?
One way is to use supplemental texts and pairings!
These texts are not novel-specific but EQ-connected, so every book group can use them:
articles
poems
songs/lyrics
art pieces
videos
stories
book excerpts
Supplementals and pairings can be used to create whole-class, lit circle-based, or jigsawed skill-focused lessons that students can then practice independently. Check out my EQ Adventure Packs for supplementals and pairings AND a choice board that can also be used for this purpose.
What might such a lesson look like?
Your EQ: what is more powerful: hope or fear?
Skill focus: writing analytical paragraphs (students hyperfocus on literal aspects of plot)
Whole group: listen to one of the songs, give kids a copy of the lyrics
Whole group: model identifying where you notice hope or fear in the lyrics; think-aloud noting which felt stronger and why
Small groups: kids continue identifying examples of hope & fear in the lyrics
Small groups: kids note whether “hope” or “fear” was stronger in each example
Small groups: select two lines/stanzas that best illustrate hope or fear
Post on Padlet
Whole group: debrief; model what a “good” reflection looks like; show a skills progression
Independently: kids draft a paragraph reflection on whether they felt fear or hope was a more powerful idea in song and why, using evidence from any of the groups’ findings.
This is just one way EQ-focused lit circles or book clubs can be rigorous while meeting kids where they are. The work they do in a lesson like this does not have a right or wrong answer; the kids discuss and rehearse their ideas and thinking aloud before they put pen to paper. The EQ requires kids to think beyond plot and surface-level similarities to do this work; it pushes them to consider ideas that are bigger than a text alone.
Listen in here to get a feel for how I break down this EQ and the levels of complexity available to teachers and students with just this one question:
Believe it or not, there are even MORE reasons to lean into an EQ-centered appraoch to lit circles, and there’s a PART TWO to this blog series! Are you ready for more?
LET’S GO SHOPPING!
Books for Your Next Unit on Relationships for Middle and High School ELA
One of my favorite units to teach is a unit that focuses on relationships. It’s the perfect way to hone in on complex characterization and the layers of complexity are widely accommodating for skill level. Whether you’re building the unit to teach as a whole class novel unit or as a literature circles unit, this book list is here to save you time and energy in narrowing down the search.
why do relationships matter?
One of my favorite units to teach is a unit that focuses on relationships. It’s the perfect way to hone in on complex characterization and the layers of complexity are widely accommodating for skill level. Whether you’re building the unit to teach as a whole class novel unit or as a literature circles unit, this book list is here to save you time and energy in narrowing down the search.
Themes VS Essential Questions
For a long time, I taught theme-based units: units were based on a teacher’s pre-selected theme and all of the learning was connected underneath the umbrella of the theme. I really liked the sense of connectedness, and quite honestly, I was craving that coming from a much less organized situation when I began my career. But no matter how hard I tried, I couldn’t shake the teacher-centeredness of this approach. The students had very little investment in the choice of the theme, and the direction of the conversation around the theme, and so much of it was tied to the teacher’s decided trajectory for the unit.
Inquiry, on the other hand, gave me the chance to use the best parts of themes, but deepen them and hand them over to students. Inquiry takes a thematic idea, roots it in a question, and then asks students to spend the duration of the unit investigating and exploring potential answers to that question as they progress toward the summative. Look at it this way as a “unit makeover” :
BEFORE: Unit 1: Relationships
AFTER: Unit 1: Why do relationships matter?
The thematic/topical unit states the focal point of the unit and we can assume that each of the texts in that unit will reveal different types of relationships. The inquiry unit will do those same things as the thematic unit, but nudges students a massive step further: why do they MATTER? Yes, many different types of relationships exist, but what do they do for the progress of humanity? Do we need them for survival? What are the kinds of relationships we need in our lives and which are the ones that we need to actively distance ourselves from? This one big question begs dozens of smaller ones and sets up a unit that is connected, but also divergent. A unit that is unified, but also ready to twist and turn with student curiosity. In the video below, I give a big longer take on the ways this question opens up possibilities within a unit:
Scroll through the list below of titles that are absolute perfection for this particular unit. Bookshop.org is a wonderful partner working to bring business to small, local bookstores, so if you can swing it, shop the list directly and you’ll be able to help out bookstores in your area!
What other books would you add to this list? I know there are so many that fit this EQ so perfectly and it was hard to keep the list manageable. I’d love to hear your additions in the comments!
let’s go shopping!
22 Teacher Favorites: Poems for Social Justice
Poetry is one of my favorite vehicles to have these critical thinking discussions about social justice. The voices in poetry are so raw, real, and products of the moments from which they came. This list of 22 came from talking to teachers online about their favorites to use in the classroom, as well as my own experience teaching poetry and creative writing.
Through poetry and song, many important movements have been carried through the power of the artistic spoken word. As we work to bring critical thinking and social justice into our classrooms, we not only are providing a powerful content area for skill building but also actively working to support the social and emotional learning of our students as they attempt to figure out the complicated world in which they live.
Poetry is one of my favorite vehicles to have these critical thinking discussions about social justice. The voices in poetry are so raw, real, and products of the moments from which they came. This list of 22 came from talking to teachers online about their favorites to use in the classroom, as well as my own experience teaching poetry and creative writing.
If you’re not sure what do to with a poem, I can help you sort that out:
IDEAS FOR A THEMATIC GROUPING OF POEMS:
Study a group of poems under the same Essential Question and work on building their literary analysis skills using The Big Six
Use this list to update or supplement your poems for Poetry March Madness
Use these poems to supplement an already existing novel unit as a missing voice, a voice to add complexity, or to mirror a character in the novel
Use these poems to create a Digital Poetry Choice Board
Use these poems for imitation: read, discuss, then attempt to recreate a style, a turn, a particular poetic device, etc.
And if you’re ready for an even deeper dive into the power of poetry, I’d love to have you join us in the Teaching Poetry & Creative Writing Workshop! It’s completely virtual and asynchronous, so come in anytime and gain dozens of new ideas and insights into your own practice.
And now, on to the list! Be sure to leave a comment below with additional suggestions and your own experience teaching these poems — your work is so inspiring!
“The Hill we climb” by Amanda Gorman
This poem was hot in the spotlight for the Presidential Inauguration of 2021, but it’s power has not lessened since then. I love the versatility of this poem: study it as a poem in isolation or look at it as an argument with a rhetorical analysis angle! If you need a lesson plan for analysis, I’ve got you covered:
2. A Wreath for Emmett Till
Picture books can be an amazing way to engage students in a lesson, and several teachers have reported that this one if a brilliant overlap between poetry and social justice.
3. “This is America” from childish gambino
This one is not recommended for younger students, but if you have some older students ready to dig into both the poetry of this song and the visual experience of the music video, you’ll have one of the most engaging, important lessons of your career.
4. “LET AMERICA BE AMERICA AGAIN” BY LANGSTON HUGHES
Of all Hughes’ poems, this one was always the one that most resonated and moved my students. It’s rich with imagery and allusion and I recommend taking your time with this one — it’s not a single class period lesson.
5. “IF WE MUST DIE” BY CLAUDE MCKAY
This poem is haunting and a beautiful study in tone and theme. I especially enjoy Kevin Young’s discussion of the poem and his beautiful performance, too.
6. “CITIZEN ILLEGAL” BY JOSE OLIVAREZ
I’ve had the true pleasure of meeting Jose Olivarez back in my days of working with Young Chicago Authors and Louder Than a Bomb, and I can say for certain, this work resonates with students. It’s certainly powerful for me, but whenever I put his work in front of students, something magical truly happens.
In this stunning debut, poet José Olivarez explores the stories, contradictions, joys, and sorrows that embody life in the spaces between Mexico and America. He paints vivid portraits of good kids, bad kids, families clinging to hope, life after the steel mills, gentrifying barrios, and everything in between. Drawing on the rich traditions of Latinx and Chicago writers like Sandra Cisneros and Gwendolyn Brooks, Olivarez creates a home out of life in the in-between. Combining wry humor with potent emotional force, Olivarez takes on complex issues of race, ethnicity, gender, class, and immigration using an everyday language that invites the reader in. Olivarez has a unique voice that makes him a poet to watch.
7. “NOT AN ELEGY FOR MIKE BROWN” BY DANEZ SMITH
This is a beautiful and gut-wrenching piece about the disproportionate attention paid to the death of Black Americans. It’s very short and would work nicely in a choice board where students could tackle it independently.
8. “ODE TO THE ONLY BLACK KID IN THE CLASS” BY CLINT SMITH
This and so many more from Smith’s anthology Counting Descent deserve a spot on this list and in your curriculum. In fact, Clint Smith’s name should be on the tip of every ELA teacher’s tongue when recommending poetry about the Black American experience.
Smith explores the cognitive dissonance that results from belonging to a community that unapologetically celebrates black humanity while living in a world that often renders blackness a caricature of fear. His poems move fluidly across personal and political histories, all the while reflecting on the social construction of our lived experiences. Smith brings the reader on a powerful journey forcing us to reflect on all that we learn growing up, and all that we seek to unlearn moving forward.
9. “NATIVE TONGUE” BY MICHA BOURNES
This poem is a fascinating look at the colonization of language and othering that’s been done to Black speech.
10. “ORAL TRADITION” BY WILLIAM NU’UTUPU GILES & TRAVIS T.
William Nu’utupu Giles is an afrakasi Samoan writer, and this poem focuses on the passing down of stories and traditions through spoken word for thousands of years.
11. “SOMEWHERE IN AMERICA” FROM BRAVE NEW VOICES
In this moving poem about censorship and government control, the speakers critique the contrasting experiences of America’s youth from the books they are allowed to read in school to the histories that are not taught.
12. “BLACK GIRL MAGIC” BY MAHOGANY BROWN
In this poem about belonging and experiencing othering, Brown examines what “Black Girl Magic” looks like through her eyes.
13. “ ELEPHANT” BY JOAQUIN ZIHUATANEJO
This poem focuses on the Rwandan Genocide of the 1990’s and compares the experience of a mother losing her child to that of an elephant holding her lifeless calf. This poem is packed with emotional language surrounding a lesser taught historical tragedy,
14. “SECOND ATTEMPT CROSSING” BY JAVIER ZAMORA
In this emotional poem, Zamora depicts the immense fear, uncertainty, and loss one feels when crossing over the US border illegally.
15. “GLORY” BY COMMON
From the movie Selma, this anthem speaks of an undying hope felt by those fighting for equality during the Civil Rights Movement despite great violence and discrimination against them.
16. “BULLET POINTS” BY JERICHO BROWN
In this poem, Brown explores hate crimes in America and the violence against Black people at the hands of law enforcement.
17. “TO THIS DAY” BY SHANE KOYCZAN
Shane Koyczan, a powerful spoken word poet, delivers a close look at the lasting effects of bullying in one’s childhood.
18. “WHAT CAN A POEM DO?” BY DARIUS V. DAUGHTRY
In this poem by Darius V. Daughtry, he explores the extent to which words, and more specifically poetry, have the power to cross borders and save lives. This poem is rich with figurative language and beautiful metaphors.
19. “CHINESE 101” BY SUN LUU
Luu describes his poem with this beautiful introduction:
“An ode to my mother, to my mother tongue, and all who've given me the opportunity to exist today. This is for all those who've tried to ostracize my people, who've tried to diminish the Chinese language, and have silenced and made caricatures of Asians in America. Here, I take back my language. I take back my culture. And find the voice to speak.”
20. “MISS AMERICA” BY RAMYA RAMANA
This poem is a response to racist comments and remarks after the announcement of Nina Davuluri, an Indian American woman, as the winner of Miss America in 2014.
21. “BROWN BOY, WHITE HOUSE” BY AMIR SAFI
Safi tells the story of living in post-9/11 America and dealing with the racial stereotyping and profiling he experienced.
22. “Passive Voice” by Laura Da
In this short but powerful poem, Da draws attention to the use of passive voice when describing the history of Native American culture.
EVEN MORE RESOURCES
12 Nature-Themed Activities for Secondary ELA
There is a long history of connectedness between literature and nature. From the important role that setting plays in any given story to the prolific use of nature as symbolism, but I somehow always felt distant from the outdoors inside my classroom. Here are twelve lesson plan ideas to engage your students with nature.
There is a long history of connectedness between literature and nature. From the important role that setting plays in any given story to the prolific use of nature as symbolism, novels like Frankenstein, A Thousand Splendid Suns, Lord of the Flies, Into the Wild, and so many dystopian stories rely on multiple connection points with nature to fully understand the themes of the story. Even knowing this, I somehow always felt distant from the outdoors inside my classroom and found it a challenge to incorporate the natural world into my instruction as an ELA teacher.
In an effort to bring nature inside classroom walls, I grabbed eleven ELA teacher friends to give me their best ideas for connecting the beautiful outdoors with the work we’re doing in class.
1. Northern Lights Makerspace
One of my life-long fascinations has been the wonder of the Northern Lights. There’s something so magical and mysterious about the dancing lights, the way legend and folklore have been inspired by them, and one more incredible way that nature and literature have intertwined.
That’s why I had to finally create a project that did this same overlapping -- how might students in my ELA (read: not science) classroom be able to explore this phenomenon while still hitting ELA standards? And that, my friends, is how the Northern Lights Makerspace Project was born!
Here’s option #1: pair nature and poetry. Take the project in this direction, and students will learn about the Northern Lights and then transform that knowledge into a controlling extended metaphor for their lives that carries throughout their poem. Once they’ve written the poem, students then get to create their own chalk pastel drawing depicting their own vision of the Northern Lights.
And here’s option #2: look at other natural and cultural sites that are meccas for tourism. Examine the industry of tourism and special places like Machu Picchu, Easter Island, and small far-north communities that offer lookout points for the Northern Lights and ask students if tourism is more likely to have long term positive or negative impacts on the environment and community around these areas.
Let’s take a closer look here:
Creating opportunities for cross-curricular work has become a deep passion of mine over the years, and especially after the intense screen time and distance of COVID, I’m committed to finding creative, out-of-the-box ways for students to interact with their hands and with the world around them. Also — let’s acknowledge the need for students to have FUN! In Episode 129 of the Brave New Teaching Podcast, I chat about Makerspace, classroom transformations, and other fun activities that can reignite the energy in your classroom. Give it a listen below!
2. Leaf Lantern Poems
One of Simply Ana P’s favorite things about poetry is that there are SO many different types of poems. She loves introducing haikus as a short poem format, but another fun one to teach students about is the lantern poem.
A lantern is a 5-line poem, with the first line being just 1 syllable, and each sequential line increasing by 1 syllable, except the last line, which goes back to only containing 1 syllable. Below is an example:
Life
crazy
yet crucial
constant growth thrives
Live
It’s meant to represent the shape of a lantern or a bell, but it also looks great on the shape of leaves. Ana gives her student this assignment, where they create a lantern leaf poem and need to include at least 1 figurative language or poetic device (like alliteration in the example given).
It’s a short and sweet assignment, but it can last an entire class period because students take a while to decide on topics, break down syllables, and put together the art component of the project.
Students enjoy connecting with nature, and often say the hands-on piece is therapeutic.
3. MORE Creative Writing
Nature is a beautiful thing to explore with your students. Kristy from 2 Peas and a Dog believes that students need to be connected to nature in some capacity with their learning. It is probably not possible to connect every lesson to nature, but the changing of the seasons is a perfect time to get outside and explore.
Once a season, take your classes outside to collect found natural objects e.g., pinecones, leaves, branches, etc. These items will vary depending on your location.
After you return to class, have students select 1 of their found items to write a creative story about. Students can write about how it arrived at the location it was found, they could write about how it came there in the first place, or they could give the item human characteristics and write about it from that perspective.
Kristy loves giving students creative writing choices by turning season items into writing prompts. For example, she has asked students to write a love letter from a garden rake to a snow shovel explaining why they are in love with them. The responses were amazing. These types of creative writing prompts are so open ended that students really get to shine as they do not feel that there is a wrong answer.
For more creative writing information check out this blog post.
4. POETRY TO PROTECT THE PLANET
Years ago Lesa from SmithTeaches9to12 did a Buzzfeed quiz (well tons of them but this one stands out) and there was a question about whether you’d rather have a lovely picnic outside in what looked like beautiful natural surroundings or be on a blanket in a living room that was not so beautiful. Let’s just say the indoor picnic was tops! While she isn’t much for the outdoors, Lesa is a strong advocate for environmental causes and a need for change to protect our communities.
With that in mind, Lesa, in among her many poetry lessons–check them out on her blog–incorporates spoken word that is decidedly pro-environment.
Here are four options to use in your class:
You can use these performances anytime of year but if you want to tie your curriculum to specific moments then Earth Day in April is great since it also coincides with National Poetry Month.
Watch the video to do a notice and note. What do they notice about the performance? Make (jot) notes.
What are the environmental tie-ins with the piece? In what ways does it encourage the audience? Depending on time and your group of students, you can expand this reflective activity to encourage students to take action.
Get student to dive deeper into the poetic aspects - rhyme, rhythm, figurative language. Use the full text versions to help with this.
You can check out the full lesson plan with teacher answers that Lesa created for these performances.
5. PLAY WITH PERSPECTIVE
“Get your snow boots on and let’s go!” Mom would shout as the snow continued to fall from the winter sky. For Krista from @whimsyandrigor, this formed the basis of many memories growing up in the Midwest. As she and her family trudged through the snow, dragging sleds and carrying a thermos of extra hot, extra chocolate-y cocoa to Valley View Park, sometimes she would stop and notice all the boot prints in the snow.
Reflecting back, Krista realizes maybe she was also imagining what it felt like to walk in those boots. By stepping in the literal prints of another person, her vivid imagination would run wild-Were their toes as cold as hers? Were they holding someone’s hand? Would they rather be in front of the fireplace with a good book?
As a middle school English teacher today, Krista harnesses the power of playing with perspective in an activity called “Walk with Me.” This lesson focuses on helping students see new perspectives of either real people or fictional characters. It goes like this:
Students choose two characters that have different opinions or points of a view on a single topic. For example, Aven and Conner from the phenomenal middle-grade book Insignificant Events in the Life of a Cactus by Dusti Bowling or Will and Shawn from the inimitable Jason Reynolds’s Long Way Down.
Students choose a boot print handout for the first character they will write about. Help students to think analytically about the print they choose. What do the shoes say about the character?
Using the prompts on the handout (Where is this person going? What do they see? What are they remembering?, etc), students will write from that character’s point of view. (This could be in first- or third-person and could create an opportunity to demonstrate how switching perspectives impacts the reader’s experience.)
Students then choose another boot print handout and write from the other character’s point of view. Students should stay focused on the same topic or event explored in the first piece of writing. Push writers to dive deeply into what makes the characters different from one another in order to further refine their understanding.
For both perspectives, students will make inferences about each character and dive into the thoughts, feelings, worries, and hopes embodied within.
If you have time to extend the activity, students could have the two sets of prints meet and engage in a dialogue about the topic each was thinking about. If you teach how to write dialogue, this is an excellent way to have students practice those skills in a creative writing activity.
Krista loves a hallway display and these boot prints will make for a powerful visual. She suggests hanging prints in groups of two so other students and teachers can see the contrasting views side-by-side.
Getting students to metaphorically walk in the shoes of another person is a cornerstone to creating a collaborative and caring community. This classroom activity, rooted in close reading and detailed writing, encourages students to always consider other perspectives, both in literature and in life.
If you want more creative teaching ideas like this, hop onto Krista’s email list and get little surprises delivered straight to your inbox!
6. Serene Snowflake Studies
Before moving to middle school, Natayle spent several years as an early elementary teacher. One of the things she missed the most after her move was the hands-on crafts that were a staple in her earlier teaching years. While “crafts” may be a forbidden word in secondary ELA, Natayle found a way to incorporate them here and there in her lessons, particularly those related to nature.
One of the lessons that Natayle kept in her back pocket in December, January, and February (typically snow-heavy months in Colorado) was one on a commonly overlooked feature of nature: snow crystals. On one of those rare academic “flex” days (the day before a break, a half day, or following a snow day), Natayle had her students work through Snowflake Stations. They read about the original Snowflake Paparazzi, Wilson Bentley, watched a TEDed video on the science of snowflakes and got their hands busy making their very own paper snowflakes.
Her students appreciated the brief reprieve from their usual classroom routines while taking a closer look at a wintry wonder.
Learn more about Natayle’s snowflake stations here.
7. Book Flat lays with natural elements
Assessing a text doesn’t have to mean another essay or quiz. Samantha from Samantha in Secondary loves to shake up learning with creative assessments that work no matter what you’re reading. One of her favorite assignments is a Book Flat Lay!
SAMANTHA IN SECONDARY
“Flat lays have become increasingly popular with books, but you can see the technique used with any object, especially food or fashion items.”
A "flat lay" is a photography term for an image shot directly above an object. It includes a bird's eye view of an item with carefully curated elements surrounding it. Flat lays have become increasingly popular with books, but you can see the technique used with any object, especially food or fashion items. Samantha loves to have students curate objects based on a text and lay them out to take a photo.
Not only does this assignment lend itself to critical thinking (Which objects would be best to include and why? How do the objects directly connect to the text?), but it also provides a great opportunity to practice 21st century skills like photo editing and graphic design. Try a free platform like Canva to help your students edit their photos!
Take your students for a walk around your school’s campus to find some nature-inspired objects that could be used in their flat lays. You’ll be amazed at the creative insights they’ll gather
Looking for a done-for-you version of this activity with complete instructions, examples, and a rubric? Click here to check out Samantha’s complete resource.
8. Reading zone
After months of snow, rain, and freezing cold temps, Carolyn from Middle School Cafe looks forward to being able to spend time outside. When the temps warm up enough to spend a lazy afternoon in the park reading, Carolyn knows that spring is just around the corner!
Carolyn share's her love of reading in the park with her students by taking them outside for Reading Zone as a reward for positive behavior. Reading Zone is a magical place where students can immerse themselves in countless stories, genres, and authors. By providing opportunities for reading choice books, students will discover the true joy of reading!
Nothing motivates students more than an opportunity to go outside! By changing up the scenery and reading outside students see reading as fun and not just for academic purposes.
With choice books in hand, Carolyn leads her students to the courtyard at the back of the school. Students can decide where they want to sit - on the benches, at the tables, or even on the ground with the warm sun shining down on them. As long as they are reading, students can choose their spot.
Carolyn looks forward to many afternoons in the sun, surrounded by her students and their books! It's a perfect way to celebrate the end of winter and the beginning of a new season.
Be sure to check out this blog post for more tips and making silent reading more fun and productive.
9. literary snowman
Katie from Mochas and Markbooks works at an Indigenous high school where many of her students come from remote northern communities with strong connections to the land. Trying to find meaningful and memorable ways to connect her curriculum to the outdoors, Katie thought of the ultimate way for her students to conduct character studies in the snowy weather - literary snowmen!
If you’re lucky (or unlucky) enough to have snow on the ground, Literary Snowman Building is a cool idea to try with your students, and the best part is that your students can complete this activity at school or at home, depending on your circumstances.
The concept is simple, students build a snowman and then decorate it with items to signify a literary character.
Students can work individually or as a team and you can turn this into a fun competition by completing a gallery walk of the snowmen and asking students to vote for their favorite, or you can check out this blog post which contains a rubric you can use to assess the snowmen and determine a winner that way!
10. environmental issues bloom balls
Yaddy from Yaddy’s Room loves to use Bloom Balls as a way of getting her students involved with the environment and nature. Bloom Balls are a 3D project where students complete a task for each face of their ball based on Bloom’s Taxonomy. Yaddy’s students absolutely love putting together their Bloom Balls together and displaying them for visitors.
@YADDYSROOM
Yaddy’s students absolutely love putting together their Bloom Balls together and displaying them for visitors.
For this project, students choose one environmental issue that interests them and go deep into research, looking up facts on the environmental issue, what causes it, what effects it has, what policies have been put into practice already, who they can write to right now to tackle the issue, illustrating what the world would look like in ten years if the problem persists and so much more!
11. symbolism scavenger hunt
Olivia of Distinguished English Teacher knows symbolism is all around us, and the sooner our students realize that, the easier their academic lives will be!
One fun way to introduce symbolism is to set a timer for 5 minutes and send kids outside to find and collect natural objects like a blade of grass, a pebble, a leaf, etc.
When the kids come back in, give them five minutes to come up with a lesson they could learn from that object. Maybe the blade of grass teaches them that we should always be growing. Maybe the pebble teaches them that strength comes in all sizes. Maybe the leaf reminds them that there are seasons of life and that change can be a good thing.
As students start to see objects as more than just objects, their minds will be ready to delve into the complexity of symbolism in the literature they read.
For text-based symbolism practice, check out this fun activity!
12. “stewards of the earth” community clean-up
If you’re a nature lover, you likely have some early memories involving the great outdoors - maybe you were raised in a natural environment, or were fortunate enough to spend holidays someplace outdoors. With the growing threat of climate change, it has never been more important to help foster a love for nature with our students.
Daina from Mondays Made Easy has spent the majority of her teaching career in large cities, including Toronto and Bangkok, where the effects of pollution are quite stark. In order to instill a sense of responsibility in students, they participate in an annual “Stewards of the Earth” community clean-up. This stewardship opportunity involves time spent in nature and the shared objective of collecting trash to show appreciation for our earth.
Your community clean-up can be facilitated as a group outing, where you and your students visit a local park or green-space during classroom hours. If leaving campus isn’t in the cards for you, you can have students practice stewardship independently by picking up a piece of trash every day for a duration of time. Have students photograph each piece of trash and compile their pictures in a journal or “pollution log.” Students’ findings can be discussed in class to foster conversation about pollution in their community. Check out this free lesson on the effects of plastic waste to get the conversation started!
Whether you facilitate your clean-up as a class or independently, be sure to model safe practices to your students: ensure that they are always avoiding sharp or hazardous materials, are protecting their hands with a pair of reusable gloves, and are practicing proper hand washing after being outdoors. Speak to your science or geography departments to find out if a class set of reusable gloves can be found at your school.
Reading Sprints to Increase Student Engagement in ELA
Over the years I have tried many different ways to promote reading in the classroom including, reading logs, AR tests, and journaling. But the one way that I have found that helps my students read more and apply it to topics we learn in class is through reading sprints.
The following is a guest post written by Lindsay from @smalltownela
cultivating a love of reading
One of my biggest goals as an ELA educator, like many others, is to promote independent reading to my students as much as possible. Because of course we want them to love reading or at least enjoy it more than they want to let on. Over the years I have tried many different ways to promote reading in the classroom including, reading logs, AR tests, and journaling. But the one way that I have found that helps my students read more and apply it to topics we learn in class is through reading sprints.
LET’S TRY READING SPRINTS
Now I just want to come out and say that I am most definitely not the first person to come up with this concept because I saw it on Instagram from some of my favorite accounts (@missboverseas and @elaeveryday) and tweaked it for my own classroom.
But here is the gist if you haven’t heard of them yet:
Have your students mark down the page that they are starting on, and then you have your students read for an allotted time, usually around 8-10 minutes.
Once the timer goes off, have them mark down where they finished and then have them take a break and answer a question of your choosing.
Then, repeat the process. Usually, I only do 2 reading sprints in my class, but you are free to do more or less however you see fit.
Amanda has a reading sprints slide deck that teachers love to keep the time structured and you can grab it here.
READING SPRINTS: THE STRATEGY
When using reading sprints in your classroom, you can do multiple things in between “sprints” with your students. You can have them do a quick reflection, ask them to write a summary, or look at a different element in their reading, including tone, mood, foreshadowing, or make a prediction to name a few. The easy thing about it is you can constantly switch up the questions and then every quarter or so just reuse them because the answers and the analysis will be different because they will be reading a different novel. This helps them understand the topic that you are learning and apply it in many different ways to strengthen their skills.
The best part about reading sprints is how easy it is to implement them in your classroom on a regular basis. Not only are you building in solid independent reading time, but also having them work on skills or standards that you want them to practice more. I have found that using reading sprints in my class on a regular basis helps my class build up their reading stamina which helps when reading full class novels, poems, or close reading activities.
STREAMLINING READING SPRINTS IN THE CLASSROOM
Here are a few more ways you could use Reading Sprints in my class.
Early Dismissals - this is the best way to have a productive class when you are on an early release schedule. The students know to walk in, open up their computers and we get started right away. Usually, I try to link it to whatever standard we have been learning about that week.
Bell-Ringer - depending on how long your class is having your students do one reading sprint every day and answering a question in their journal or on Google Slides is an easy way to have them read every day while also being held accountable.
End of the Week - I personally do reading sprints on most Fridays with my students. It’s the best low stakes end of the week plan that both my students and I look forward to. We look at different skills we worked on during the week and apply them easily to our independent novels. Plus it’s an easy way to end the week and send them off with no homework for the weekend.
READING SPRINTS AND FLEXIBILITY
I love using reading sprints in my classroom and my students begin to look forward to them as well. The best part about them is you get to decide how often and how long you get to use them. This can be a random activity you do once in a while or something you do on a consistent basis with your class. I hope you can go and find new ways to use them in your classroom.
Hey! Amanda here checking in :)
Reading Sprints are another great tool to help teachers move away from plot-centered teaching. When it feels like we’re so tied to plot level detail comprehension, it can be hard to remember the big picture. As you work through building your craft and aligning your goals, I made this YouTube video to help you think through the ways in which critical thinking can show up in your lesson planning. I hope it helps!
11 Best Movie Scenes to Introduce Rhetorical Analysis
Rhetorical analysis is a skill that needs practice and reinforcement all year long. Using various moments from movies and film offer a great chance to examine both the rhetorical situation and the arguments themselves. Check out these eleven movie suggestions to teach rhetorical analysis including various Disney movies, The Notebook, and We Are Marshall.
Teaching students to write rhetorical analysis is probably one of the hardest things I had to learn as a teacher. And if you’re a teacher of rhetoric, you know exactly what I mean. If you need a deeper, more philosophical step by step guide, I have a blog post for that, but if you’re feeling good but in dire need of ideas for lessons, that’s what I’ve got for you right here.
One thing I’ve found over my years of experience in teaching rhetoric is how incredibly helpful it is to have a fictional scenario to use to teach argument. When the rhetorical situation is rich, it makes connecting the dots easier for students and also keeps them from feeling compelled to highlight and annotate a bunch of devices without understanding why.
To lend a helping hand, I’ve compiled a list of great moments from film that present opportunities to teach both the rhetorical situation as well as the arguments themselves. If you don’t already have a template to use for teaching rhetorical analysis, I’ve got you covered!
#1: “Be Our Guest” from Beauty and the Beast
This is my favorite one to use when introducing the rhetorical situation. I have a ready-to-go lesson right here if you need it!
#2: “Mother Knows Best” from Tangled
Mother Godel has a mission: keep Rapunzel locked away. But when she starts to get curious about leaving her tower, this song puts Rapunzel back in her place.



#3: “The Other Side” from The Greatest Showman
PT Barnum needs a cash infusion to make his circus dreams come true and there’s only one person that can help him. Watch this argument weave through an incredible song and grab a pre-made lesson plan here if you are in a pinch!
#4: “Going to Battle” from the Apple TV series See
The war is imminent. The odds are against them in every way. Here are two going to battle speeches that will get your students ready to go! If you need it, I’ve also got this one written for you — check it out below!
#5: We Are Marshall
There are many athletic pump up speeches out there, but this one takes place at the grave site of players that have come before them. Buckle up for this classic from Matthew McConaughey.
#6: Titanic - Don’t Jump
Jack catches Rose at her lowest point and has to convince her to rethink her situation. Use this with caution, however, because the suicidal premise may not be suitable for your group.
#7: The Notebook: Allie & Noah’s Fight
He’s already lost her once, and this time, he’s fighting to keep her around. There’s some fun language in this one, but other than that, it’s short, sweet, and memorable.
#8: Toy Story 3: Woody’s Speech
I’m going to need you to try really hard and keep it together for this final speech to Andy’s toys. In his speech, Woody tries to encourage the crew to keep an optimistic outlook on their future despite the doubters in the room.
#9: Frozen “Do You Want to Build a Snowman?”
Elsa? Wanna come and play? Sadly, she doesn’t, but that doesn’t stop Ana from trying.
#10: Grey’s Anatomy: Pick Me, Choose Me
This is DEFINITLEY the corniest (and probably the weakest) argument on the list, but that just makes it even better to pull apart. Did Dr. Grey’s speech do enough to win over Mc. Dreamy?
#11: The Phantom of the Opera “Music of the Night”
What does it take to convince a total stranger to abandon her life as a ballerina above ground and hang out with a masked main in his underground lair? Let’s see how it works out!
Some final thoughts:
I hope this gives you a good start in preparing a lesson to watch, talk about, and analyze some great arguments in movies. As always, I’d love to hear about your experiences, ideas, and outcomes in the comments below! Which films did you use? Which films did your students best respond to? Happy analyzing!
FOR MORE RHETORICAL ANALYSIS PRACTICE:
LET’S GO SHOPPING!
3 MORE Commercials for Rhetorical Analysis
Rhetorical analysis is a skill that needs practice and reinforcement all year long. Use this template and three commercial suggestions to help you get going with rhetorical analysis in your classroom.
There’s just something about commercials that make them such ripe teaching tools for practicing rhetorical analysis. The problem is, though, that it can be hard to find ones that are just right for students. In an effort to continue making more commercial rhetorical analysis ideas available to teachers, I’m stepping up my game and adding a few more to the conversation right here! Let’s jump in.
A FEW REMINDERS:
Before starting with ads, make sure you’ve covered the rhetorical situation. I have an easy and fun lesson for that ready-to-go featuring the song “Be Our Guest” from Beauty and the Beast, so feel free to use it!
You might also consider having your students familiar with SPACE CAT or another framework that you like (another might be SOAPSTONE). I dive into that a bit further with the song “Mother Knows Best” from Tangled and share a free rhetorical triangle template here, too.
If you like these commercial suggestions, you might also like this blog post with three Super Bowl ads from 2022 that is very similar to this post -- just more ads to put in your arsenal!
Rhetorical analysis is a skill that needs to be practiced over and over and over again. Too often, we are introducing ethos, pathos, and logos on repeat without ever getting much further. We know rhetorical analysis is so much bigger than labeling a few appeals: it’s about understanding the power of the message in the context that it’s delivered.
START WITH YOUR TEMPLATES
If you are new to the idea of using SPACE CAT or any other framework to guide your lessons, I’ve got you covered. When I teach RA, I like to try and consistently use the same kinds of handouts for every lesson so that students aren’t constantly learning a new way to “do” the job and I’m not constantly recreating the wheel. Here’s what I’ve created for you to try with your students:
On the one side, students are brought back to the rhetorical triangle and grounded in the rhetorical situation as much as possible. Some commercials are a bit tricky to deciper (as opposed to speeches or moment from film), but make sure they start with speaker and audience at the very minimum. Then, using these templates, students can dig into the argument itself and shade in the particular choices they notice, the appeals at work, and the tone word range that they observe in the commercial. This is a very basic starting point, but it serves as a visually clear way for students to try and see all fo the pieces of the argumetn working together AND prioritizes the use of evidence for each. You might not examine all three components every time, and that’s totally okay! Simply cross out what you’re not working on and focus on the rest.
FRITO LAY: IS IT FOOTBALL OR FUTBOL OR SOCCER?
Up first is a chip commercial and a centuries-long debate: do we call it futbol or soccer? Featuring two huge celebrities (Peyton Manning and David Beckham), Frito Lay harnessed a playful moment of intersecting worlds during the 2022 FIFA World Cup. Here are a few places that are worth spending time in your lesson and analysis practice:
SPEAKER: We have TWO speakers from two seemingly polar opposite sides of the debate. What is each man known for? What makes each of them credible in their own expertise? What kind of personality do these men have and how does that translate into the tone of the commercial? Depending on which version of the commercial you watch, there are even more celebrities in the soccer/futbol world brought into the story to lend his or her own side to the debate, deepening the roots of the history of the question. Guide students to think about the circumstances for each of the celebrities -- they are especially important in guiding the tone of the ad (I mean, who doesn’t get tickled by Mia Hamm going off on a park district referee?!)
CHOICE: JUXTAPOSITION: Beginning with the two speakers, this commercial leans into the power of opposing forces to create humor, tension, and involve a vastly large audience. The most commonly juxtaposed images are that of ordinary, everyday soccer matches (mostly for kids) against massive stadium-sized matches with thousands of roaring fans. Beckham even jokes about the size of the World Cup as an insult to Manning’s/American football’s Super Bowl. The celebrity spokespeople are juxtaposed against each other or the other person they’re debating the word with (think Mia and the ref). And here’s the thing -- even though the opposing forces are strong, it’s FRITO LAY CHIPS that brings everyone together in the end. The brand is the unifying force, no matter which side of the debate you might find yourself on.
APPEAL: PATHOS: Largely, the inclusion of memorable celebrities (Brandi Chastain, Mia Hamm, etc.) and their playful banter aim to create an emotional experience of togetherness and unity. The commercial seeks to acknowledge a divide (playfully), but then warmly reminds the audience of their shared love for the world’s game. The brand is featured affectionately as a witness to all of these events and ultimately as the one thing that everyone can agree on.
TONE: The tone of this commercial fits anywhere in the light, happy, and even trustworthy side of the circle of emotions. Students could defend several tone word combinations, especially looking at the use of banter, sarcasm, and overall humor.
The All-New PlayStation Plus: Why be one thing, when you can be anything?
CHOICE: IMAGERY: The commercial begins in public, in daylight, in a diner. Slowly, the narrator moves from the outside world, into his home, and deeper and deeper into spaces inside that (presumably) the outside world never sees. The commercial is mostly dark and focused on these interior spaces that are sprinkled with the unexpected and fantastical (what was that fish in his fish tank?) As each scene (image) draws the audience deeper into the narrator’s home, we’re experiencing what Playstation is suggesting it must feel like to have this rich, inner life of fantasy and imagination through their gaming experience.
You might also talk about juxtaposition and the use of rhetorical questions, too.
APPEAL: ETHOS: While certainly the commercial is emotional in terms of the excitement and tension building around where on earth that huge slab of meat is going, it would be interesting to talk to students about how Playstation has also created a scenario in which they are the trusted brand to bring this kind of imagination to the audience. They’ve presented a fantastical scenario, one that many might feel envy or hope to experience themselves, and by dropping small hints of each of the games they’re best known for, they’ve also created a powerful sense of credibility as the providers. The layering of images from the various games works to develop trust that Playstation will give its players this incredible experience.
TONE: With a series of reflective rhetorical questions and a blurred line between reality and fantasy, Playstation has created a curiously inspired tone in this commercial. It’s a bit jarring and it’s a commercial that makes the audience wonder what just happened?. The placing of items such as the astronaut helmet in the closet leaves the audience trying to connect a series of dots -- they’re constantly wondering what’s coming next. This sense of curiosity and wonder reflects the experience that Playstation hopes its audience will have while playing their games.
FLAMIN’ HOT DORITOS & CHEETOS: “PUSH IT”
RHETORICAL CHOICE: Incongruity & Reversal: If this is the time to start talking bout techniques of humor and satire, you might consider placing these two at the table: incongruity and reversal. Before digging in, a quick reminder: “correctness” is less important than the critical conversation around deciding on a best choice. These two techniques are challenging, and the last thing we want to do is present something that add to the impression that rhetorical analysis is as simple as “device hunting”. That said, if this is part of a larger conversation about humor in rhetoric or satire in communications, this commercial would be great to use to flesh out the ways in which the commercial’s core technique would be considered incongruous or reversal. In this particular example, I think it’s helpful to have students focus on the subject rather than the characters: the Doritos and the Cheetos. How is the subject handled? When examined this way, I think a strong argument could be made for incongruity. I like the way ReadWriteThink breaks it down here if you’re looking for a reference.
APPEAL: PATHOS: The composition of the commercial is aimed at creating a comfortable and lighthearted relationship with the audience. The use of cute, animated jungle creatures? Adorable. The fun throwback song? So adorable. The look of surprise on the hiker’s face as the sloth drags away a bag of Doritos? So funny. The commercial relies on the absurd scenario to break down any defenses and create a memorable, humorous connection between the brand and the audience.
TONE: While there’s not much dialogue to dissect here, this is a great opportunity to have students look at tone through music. The popular song from Salt ‘n’ Peppa used here has been reduced to just a fraction highlighting the catch phrase -- what is the effect? How does it create such a humorous scenario?
Some final thoughts:
I hope this gives you a good start in preparing a lesson to watch, talk about, and analyze some great commercials. As always, I’d love to hear about your experiences, ideas, and outcomes in the comments below! Which ads did you use? Which ads did your students best respond to? Happy analyzing!
FOR MORE RHETORICAL ANALYSIS PRACTICE:
LET’S GO SHOPPING!
Teaching Rhetorical Analysis: Using Film Clips and Songs to Get Started with SPACE CAT
Try beginning your rhetorical analysis lessons by focusing on the rhetorical situation before heading into deeper analysis. When you’re ready, dig in using SPACE CAT and a great song from a musical that has a premise and an argument to examine. Here’s what we’ve done in my class using “Mother Knows Best” from Tangled.
Rhetorical analysis: so much more than commercials and appeals
Rhetorical analysis can get a stuffy reputation. Sometimes, we reserve it only for “serious” classes and students and we focus on monumental, world-shaking types of speeches. While this approach accomplishes a few of our long-term goals for education, it’s not doing enough to reach the masses of students who need these skills.
I hope you’re here reading this because you want to try RA with seventh graders. You want to introduce rhetorical analysis to your struggling 10th graders. I hope you’re here because you’re trying to do RA even though you haven’t been deemed worthy and been exclusively anointed as an AP Lang teacher. I hope you’re an AP Lang teacher here looking to do things with a broader scope and new entryways into conversations about complexity and sophistication.
Really, I’m glad you’re here.
RHETORICAL ANALYSIS: THE BASICS
Here’s where we need to start: the triangle.
Rhetorical analysis is less about appeals and more about the unique connection between three points: the speaker, the audience, and the message.
When we start RA zeroing in on ethos, pathos, and logos, we are playing a bit of a dangerous game. Teaching terms can be a comfort zone for teachers (we do this with figurative language, too). In our field, there are so few direction instruction content types of lessons, that it can feel cozy to snuggle up with a list of terms we understand and deliver them to our students. Without realizing it, we’ve created a pretty deep hole, jumped in, and forgot to throw down the rope ladder for when we need to get back out.
When we start with terminology, we’re sending the message to students that this is the primary focus of analysis: identification. We’ve armed them with dozens of terms, so the goal of analysis must be to slap these labels all over a speech and call it annotation. Then? It ends. Students falsely believe that they’ve accomplished the task because they did exactly what you taught them. They found the rhetorical questions. They found a simile. They found an example of ethos.
And then? We get really frustrated when they can’t tell us WHY, HOW, or SO WHAT when we probe them deeper about what they’ve identified.
This is my very long way of telling you this: DON’T start with terms, or, if you do, be ready to pivot quickly!
RHETORICAL ANALYSIS: WHERE TO BEGIN
START with the rhetorical triangle or a framework that you like (I like SPACE CAT) and a conversation around the rhetorical situation (SPACE). By emphasizing the importance of understanding the components of the broader context of the argument, we help students start the probing question why? in the back of their heads as we go deeper and deeper into the argument itself.
One of my favorite pieces to use for practicing the rhetorical situation is looking at Lumiere’s plea to Belle in “Be Our Guest”. In another blog post, I outline how much there is to the situation -- there is so much to consider in terms of the speaker, the purpose, the audience, the context and the exigence. In the slide deck for this lesson, we spend a great deal of time listing as many details as possible before even looking at a single lyric. Why? Because once we get into the argument, we’re seamlessly moving through true analysis.
Ms. C? I think I found a simile.
What similie is that?
Well it says ____________.
Hmm.. You’re right. So why does this particular simile hold weight knowing what we know about who Lumiere is and what he’s trying to achieve in this moment?
Wheels turning…
RHETORICAL ANALYSIS: GETTING INTO THE ARGUMENT
So we’ve got a handle on the rhetorical situation. That’s a win. In fact, that might be the entire goal of a unit if you’re just beginning. If your school is taking their time and truly working on vertical articulation, this is a great skill to introduce at 9th grade and build toward mastery in 10th.
But let’s say we’re moving on a bit and ready to analyze the argument. You might have a speech, a commercial, another song, or another type of fictional scenario, and now we need to look at the techniques used and do the analysis work.
This is where we come back to our analysis framework. I like using SPACE CAT, so this stage is where I rely on CAT: choices, appeals, and tone.
Rhetorical choices include just about everything, so it’s up to you to narrow the lane of what each argument is doing well. A rhetorical choice might be the structure or organization of the argument, an extended metaphor, the use of personification, or even a particularly interesting use of parallel structure. Appeals are what you think they are: ethos, pathos, and logos. And of course, tone is exactly what you think it is, too.
Not all choices, appeals, or potential tone words are important to talk about in every speech, so fully embrace your right to decide ahead of time which choices are on the table for discussion (this is called scaffolding and if you need help with it, I have a training in my Mastering Close Reading Workshop that you might find very helpful!).
Let’s Look at an Example: “Mother knows best”
Here’s a quick example from “Mother Knows Best” in Disney’s Tangled for each of the components in CAT.
Mother Godel opens her song referring to Rapunzel “as fragile as a flower; still a little sapling, just a sprout”. She’s comparing Rapunzel to an undeveloped, extremely young plant.
She then uses the refrain “Mother Knows Best” along with other overly-assertive physical behaviors to assert her own ethos and Rapunzel’s lack of life experience.
The song also gives students the chance to look at tone, especially in the verse where Mother Godel tells Rapunzel that she won’t survive as a “sloppy, underdressed, immature, clumsy” and “gettin’ kinda chubby” girl out in the real world. This demeaning tone further underscores Mother Godel’s authority and increases the fear in Rapunzel about leaving her tower.
RHETORICAL ANALYSIS: SO WHAT?
Well, we’ve arrived back where we started, friends. There’s a whole lot of highlighting, lots of phrases and details identified as one thing or another, but here comes the real work: SO WHAT?
So, Mother Godel uses a demeaning tone toward Rapunzel. So what?
She compares her to a “sapling” that has just sprouted from the ground. So what?
Here’s where we send students back to the rhetorical situation.
Support them through their “so what” with questions referring back to SPACE:
Why is this tone effective given what we know about the audience?
How does this metaphor create a sense of fear in Rapunzel?
How does Mother Godel’s use of hyperbole help her achieve her purpose?
Given the context of the situation, why would Mother Godel rely on the emotion of fear in this particular argument?
Once you’ve gotten through the SPACE, the CAT, and now arrived at the analysis part, remember that you can do this a few ways. Students oftentimes will write a paragraph of analysis, but if you’d prefer, you might have students complete a one-pager or just have a discussion that outlines what students could write about. It’s okay for some lessons to be heavier on the process than on the result.
SOME FINAL THOUGHTS…
RHETORICAL ANALYSIS: TRUST THE PROCESS
This is the process. It takes time, practice, and more practice. But if you are able to confidently lean on a framework that you like, provide the right types of arguments that meet students where they’re at, and stretch their work with rhetoric over multiple years, you’re going to find increasing success.
If you’re looking for more support, I have resources that are ready to help you. Keep doing the work -- I’m right here behind you every step of the way.
LET’S GO SHOPPING…
Three Myths about Close Reading
Close reading is often confused or made synonymous with things it most definitely is not, making it seem too scary to even approach. Maybe you’ve tried it, hit a wall of frustration and abandoned-ship. Well, it’s time to replace frustration, uncertainty and fear with the truth, and bust three common myths of close reading.
Three Myths about Close Reading (Busted!)
Wait, what? Close reading? That thing in Common Core everyone says they do but can never actually explain? If these sound like your thoughts, you’re not alone. And here’s why:
Close reading is often confused or made synonymous with things it most definitely is not, making it seem too scary to even approach. Maybe you’ve tried it, hit a wall of frustration, and abandoned-ship.
Well, it’s time to replace frustration, uncertainty and fear with the truth, and bust three common myths of close reading.
Three offenders.
Three stories that have run amok doing what myths do best – attempt to explain what we don’t understand.
But the thing is, close reading CAN be explained and understood, and there is a close reading reality. Let's talk THAT reality, so you can see the power this instructional strategy has to transform both your teaching of reading and your students’ growth and confidence.
MYTH #1: Close Reading = Reading an Entire Text
If the thought of figuring out how to teach a close read of an entire short story, or
an entire chapter OR
an entire article OR
an entire scene
gives you hives, well, that’s fair. It should!
If telling your classes to “do” a close read of X story results eye rolls, audible groans, and no sense of whether students are actually practicing reading skills – also fair.
This idea that close reading means scrutinizing an ENTIRE text is a complete and total, well, MYTH! It is also a recipe for overwhelm for both teachers and students, with little to no benefit for students’ growth as readers. Reading an entire text is just that – reading. And while there is nothing wrong with “just reading” that is not the purpose of close reading.
HERE’S THE REALITY: Close Reading = Reading a Passage
Close reading is re-reading with intention, with the purpose of practicing skills, learning patterns and deepening understanding. So instead of an entire text, choose passages no more than a page long, maybe going onto the back, for your lessons.
Begin by having students read a longer chunk: a chapter or chapters, an act, a short story – either for homework or independently during class – of which the passage is part. When the kids come to the close reading lesson, it will be at least their second encounter with said passage.
Pffft, you might be saying. My students aren’t going to read that longer chunk independently.
That might be true. But they can still do the lesson.
Close reading lessons are always in-class, skill-focused, teacher-directed experiences. Keeping the passage short allows students to do the lesson whether or not they completed all of the prior reading. The passage is read, and often re-read, in class, so you know, at the very least, even if students read nothing else for an entire unit, they have read those close reading passages and practiced skills.
Length is critical, and to keep passages short, it is not only ok but necessary to eliminate content that does not help students practice the skill. Consider what is most important and what is necessary for student practice. Then decide how much to include before and after. Context can always be provided by you for the kids in the lesson directions.
MYTH #2: Close Reading Prioritizes Reading the Whole Text
Your reading curriculum contains four core novels and a Shakespearean play. The best way for students to grow as readers, writers, and thinkers is to make the text central to learning. They must read every page and every word of every novel and the play in order to make progress. Frequent comprehension quizzes are the way to keep them accountable.
Close reading is reading EVERYTHING – page one to page end.
Um, no. Just NO. To ALL of that.
HERE’S THE REALITY: Close Reading Prioritizes Skills
Close reading DOES NOT – like, to infinity DOES NOT – center the text.
Close reading centers SKILLS.
The text is the vehicle through which skills are taught. Don’t get me wrong, the text is important, but students are not being assessed on whether or not they “know” the whole text. They will be assessed on the skills you taught and that they practiced during your close reading lessons.
Skills can run the gamut – from rhetorical situation to recurring symbols, to use of imagery – depending on the type of text, your essential question (more info on this here), and your summative assessment. The skills determine the annotation focus(es). Remember, though, not to get carried away in asking students to annotate for all the things. Less is more.
Make it super clear in your directions what you want them to annotate for. Without this, students end up randomly highlighting and labeling with no sense of how or why it all fits together. Instead of wild goose chase annotation, send students on a purposeful, scaffolded path toward analysis.
MYTH #3: Close Reading Answers A Set of (Text-Dependent) Questions
You are at the photocopier and find a handout titled, “Close Reading Questions.” You look through it and consider that maybe this is close reading.
Nope. Not even kind of.
HERE’S THE REALITY: Close Reading Works with Essential & Analysis Questions
A list of teacher-created questions for students to answer as they read a text – or after they read it – could maybe be considered “guided” reading. But it is not close reading.
Close reading does involve questions, but they are of the essential and analytical variety. And you come up with them before students close read anything. These are the questions that drive your unit and skill focus. They are the questions that inform your backwards planning: what it is you want students to know or do by the end of that unit?
Your close reading lesson passages should all connect to your unit essential question (more on EQs here), so that they build on each other, which results in students building their learning – comprehension, pattern recognition, deep thinking – over time.
And within each lesson, you create an analysis question for students to work with at the end. When planning a close reading lesson, come up with this question first. Consider what you would look for in the passage to answer it. This will help you come up with student annotation guidelines. Having kids draft a skills-focused analytical paragraph to answer a question using their close reading annotations helps prepare them not only for a summative task, but makes them derive meaning, instead of searching for a “correct” answer.
So, yes, questions, BUT questions that require students to make meaning using the skills they practiced in that close reading lesson for that particular passage, not to hunt and peck through an entire text to find “the answer.”
SOME FINAL THOUGHTS…
Close reading is not its mythology! It is not reading an entire text, it is not whole-text centered or answering a set of text-dependent questions. Close reading reality decenters the text, prioritizes skills, and uses essential and analysis questions to drive learning. This instructional strategy has the potential to move mountains for your students as readers, writers and thinkers and for YOU as a teacher of reading.
If you haven’t tried close reading before in your classroom or if you’d like to revisit it after a less than positive experience, grab this free video where I go into more depth about the what, why and how of close reading. What has been your experience with close reading? What questions do you have?
LET’S GO SHOPPING…
How to Throw a Gatsby Party as PreReading Strategy
Teaching The Great Gatsby is a massive task, but setting up students during prereading is a critical moment to help them feel successful as they’re tackling the novel from the start. Here’s how to use a Gatsby Party as a stations activity that helps students get to know each of the major characters in the novel.
How to Throw a Gatsby Party as PreReading Strategy
There is no shortage of blog posts in the world about English teachers throwing Gatsby parties for their classes before or after their study of the great American classic. What I want to show you here is how you can use this party as a gateway activity to the book and a prereading strategy that sets students up for early success in reading. So, instead of waiting until the very end of the unit to celebrate, let’s start things off with a classroom transformation that will engage students from the start!
Shop all of my Gatsby party essentials on my Amazon Storefront
WAIT! DO YOU HAVE A COLOR SYMBOLISM TRACKER TO USE FOR YOUR UNIT? GRAB THE ONE PICTURED ABOVE RIGHT HERE AS MY GIFT TO YOU!
SHOULDN’T PARTIES BE FUN?
Yes! No matter when, where, or how you throw your party, there should be plenty of fun. Of the many goals of the party, getting students hyped up to read and feeling the energy of the story, is a huge priority. If you have some money to spend, spend it on items that can be reused for a few years -- that makes the investment worth it. You’d be surprised at how a Dollar Tree raid can add up and then at the end of the party all get thrown away and be completely disposable.
Era costume pieces, tapestries to hang as backdrops, photo props, or even centerpiece items from thrift shops are things that can be packed up and used year after year. I like these posters ($10) and once they’re laminated, they’ll last forever. Here is a huge collection of ideas that I have stored on my Amazon Storefront — I like to use this as a vision/mood board while brainstorming what I’ll do each year.
If you’re not going to spend any of your own money, there’s plenty to do to set the mood for free: YouTube playlist of music from the movie or Jazz Age music, cover your whiteboard in hand-lettered quotes, grab white paper from the supply closet for tablecloths, etc. I even make my students invitations to the party and hand them out a few days ahead of time. Most of them look at me and roll their eyes, but enough of them appreciate the dorky gesture.
Embrace the Thematic Tie-ins
The Great Gatsby is rife with themes that resonate with students - the American Dream, social class, love, and the illusion of happiness. Use the party as a springboard to introduce these themes in a subtle yet engaging way. Consider incorporating décor or activities that hint at these concepts. For example, you could have a "Dream Wall" where students write their aspirations before they’ve even started their discussions about dreams (and their potential to inspire or destroy). By weaving these themes into the party, you're not only setting the mood but also planting seeds of inquiry that will bloom as students delve into the text.
PREREADING WITH STATIONS
Now that you’ve set up the energy and atmosphere of the party, it’s time to do the behind-the-scenes work of getting students ready to read. For those of you reading this post who prefer to do your party at the conclusion of the novel, consider moving it to the beginning of the unit instead.
HERE’S WHY YOU SHOULDN’T WAIT:
Authenticity & Joy: Classroom transformations like a Gatsby party serve as a seamless way to pique interest in an authentic way.
Frontloads Key Information: By introducing students to the characters, setting, and themes at the outset, you give them a foundation to build upon as they read. This empowers them to make connections and comprehend the text more deeply.
Creates Anticipation and Excitement: A party atmosphere generates buzz and curiosity about the story, making students eager to dive in and discover what unfolds.
Sets a Collaborative Tone: The interactive nature of stations encourages discussion and teamwork, establishing a positive learning environment for the unit.
Enhances Engagement from the Start: Immersive experiences like a Gatsby party are more memorable than traditional introductions, capturing students' attention and motivating them to actively participate.
Builds Schema: The party helps students connect their prior knowledge and experiences to the novel's context, making the content more relatable and accessible.
As I set up my room, I create 5-6 large tables that I’ll use as the stations. This blog post will walk you through everything that I do in my lesson which can be found here completely ready for you to print and use!
Never used stations before? I’ve got a quick and easy guide to using stations here as well as how I use this learning strategy for back to school here!
Designing Stations to Support Readers
Whether you’re doing prereading stations for Gatsby or any other book, you need to consider what students need to support their reading experience. In the case of Gatsby, I’ve found that the earliest struggle students have with the novel is knowing who is who. Because of this, four of my stations are designed as “Meet the Character” stations. I pull a passage of description of Nick, Gatsby, Tom, and Daisy. At each of these four stations, students read the passage “meet” the party guest, and then jot down a record of their initial impressions of who they just met at the party.
This is a quick (but important) prereading exercise disguised by fun. In the passage selected for each character, students are getting:
Familiarized with Fitzgerald’s language
Context around each character’s personality
Basic characterization
These may seem like small things, but in the world of reading comprehension, they’re critical. Imagine reading Gatsby for the first time completely blind to the story. Now, imagine reading it witht the mood of the party that you’ve created and an initial understanding of the personalities and roles of each of the main characters. This is a huge win!
OTHER NON-CHARACTER BASED STATIONS
The other stations are flexible. Here are a few other ideas I’ve used:
Shop my Amazon Idea List
Book Cover analysis: have students look at various different versions of published book covers. What does the art reflect about the focus of the story? How does the artwork make you feel in terms of what mood you’re expecting to encounter? What are the colors used in each? How might that be reflective of the story you’re about to read?
Setting analysis: Choose 1-2 passages that capture important setting descriptions. Where will this story take place? How does the energy of the setting match or seem different from that of our “Gatsby Party” atmosphere? What are the colors, textures, sounds, smells, and visuals included in the description? You can even have students attempt to draw exactly what they’re reading in the description for an added “party game”.
Music/lyric analysis: Pull a Jazz age song and its lyrics for students to read and analyze. What were the values of this type of music? What did the music center? What kind of energy does this music give?
Trailer analysis: Set up one table with several of the Gatsby film trailers pulled up. Students can compare and contrast, make predictions, etc.
The Mysterious Gatsby Station: Compile a collection of rumors and gossip about Gatsby from the novel. Have students read these snippets and create a "Wanted Poster" for Gatsby, highlighting his enigmatic persona and the questions surrounding him.
Symbolism Scavenger Hunt Station: Hide various objects around the room that symbolize key elements in the novel (e.g., a green light, a clock, a pair of eyes). Have students find these objects and speculate on their potential significance.
Roaring Twenties Slang Station: Provide a glossary of 1920s slang terms. Have students translate a few passages from the novel or create their own "flapper" dialogue.
The Ripple Effect
Remember, the Gatsby party isn't just a one-off event. It's a catalyst for deeper learning and engagement. The enthusiasm and curiosity generated during the party will carry over into your subsequent lessons, making the study of The Great Gatsby an unforgettable experience for your students. Don't be afraid to get creative, think outside the box, and tailor the party to your students' interests and your teaching style. By setting the stage with a memorable and meaningful experience, you're paving the way for a literary journey that will stay with your students long after the final page is turned.
If you’ve been partying at the end of reading Gatsby and still love it, by all means, continue to do what brings you joy! But I do hope that at the very least, these character stations activity will provide a strong foundation for your readers at the start of the study of the novel. I’d love to hear about your experiences in the comments below!
Ready to think more through the Gatsby reading experience? Watch below!